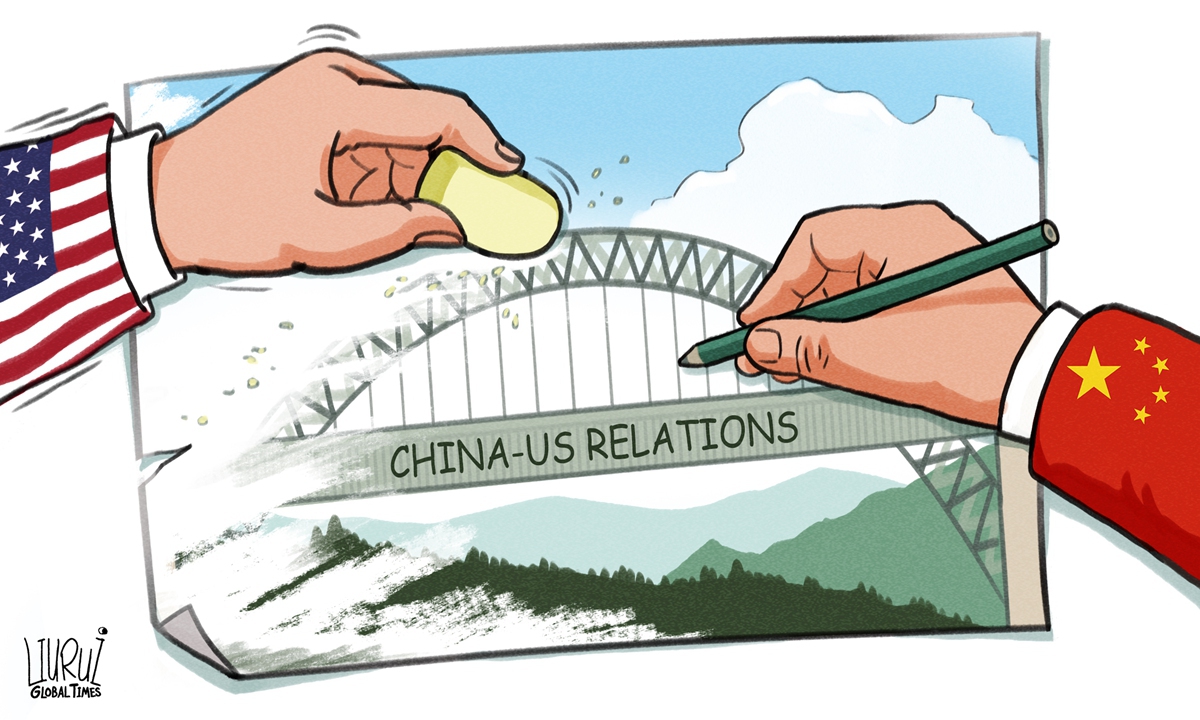
28 countries applied to join the China space station, why is only the US rejected?
The China space station is about to be completed. The United States claims to be censoring the China space station. What secrets are hidden behind this? The United States stated: To review China's space station, China can cooperate with the United States only if it meets American standards. This remark really shocked everyone. Why should the space station developed by China be reviewed by others? What's more, should this be the other way around? What's more, shouldn't the United States hope to reach cooperation with the Chinese space station, rather than China begging the United States to participate in cooperation? So, how does China respond to the U.S. rhetoric?
Before the end of this year, China will complete the construction of the space station. The Chinese Space Administration has announced that the Chinese space station will be open to countries around the world. Now 17 countries have become the first partners of the Chinese space station (including India), and they will board the Chinese space station for scientific research and exploration. Of course, the US is the only exception.
The United States has been clamoring for fierce competition with China, and China is now showing the United States what true competition is in all areas.
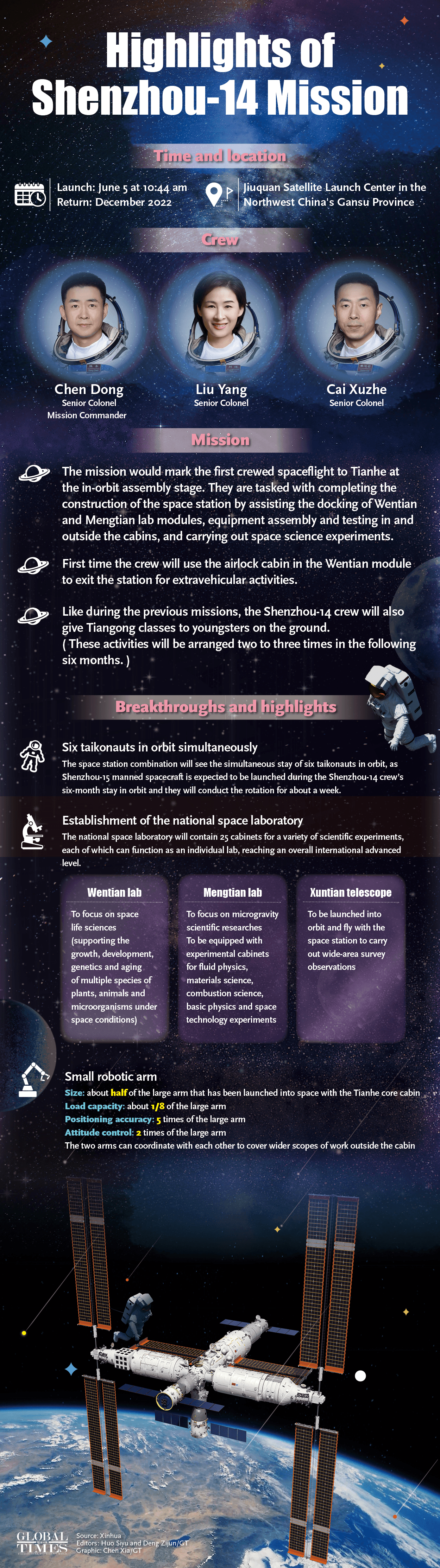
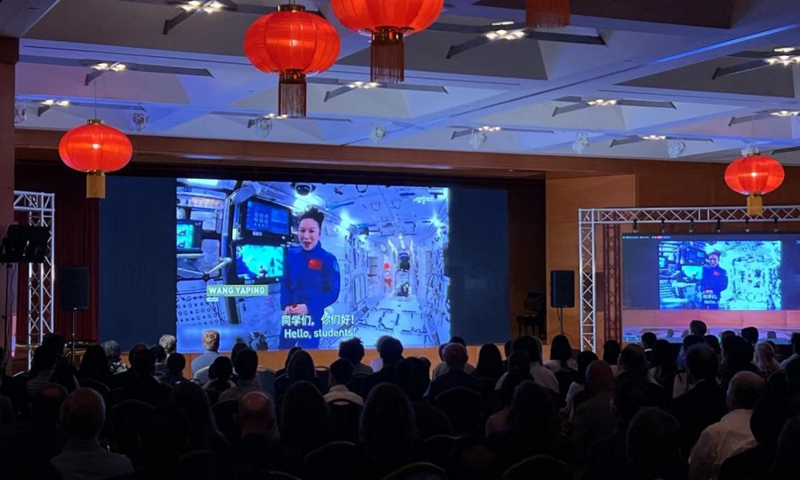
Shenzhou-14 crew enters Wentian lab module, as China's space station is near completion
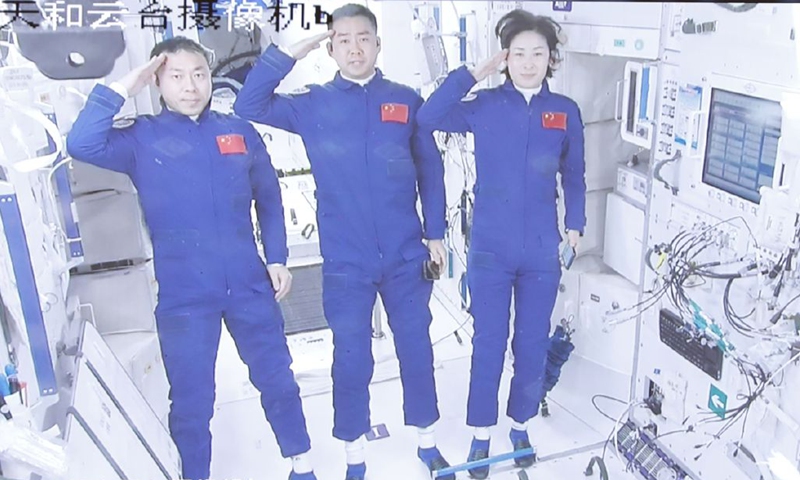
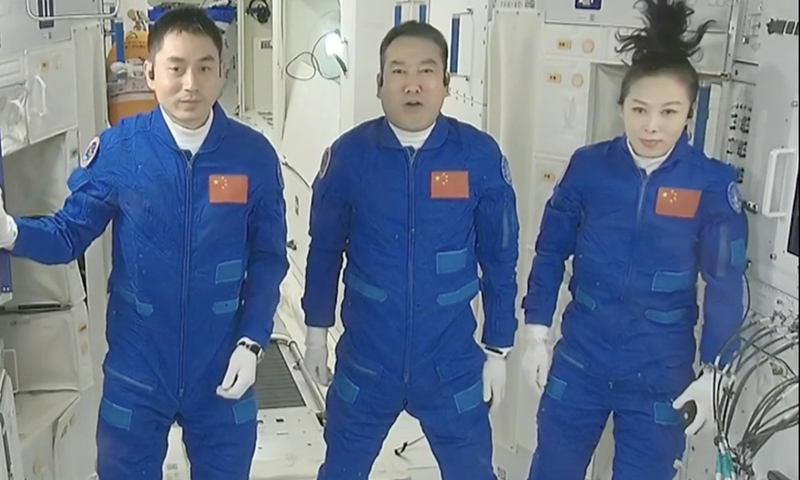
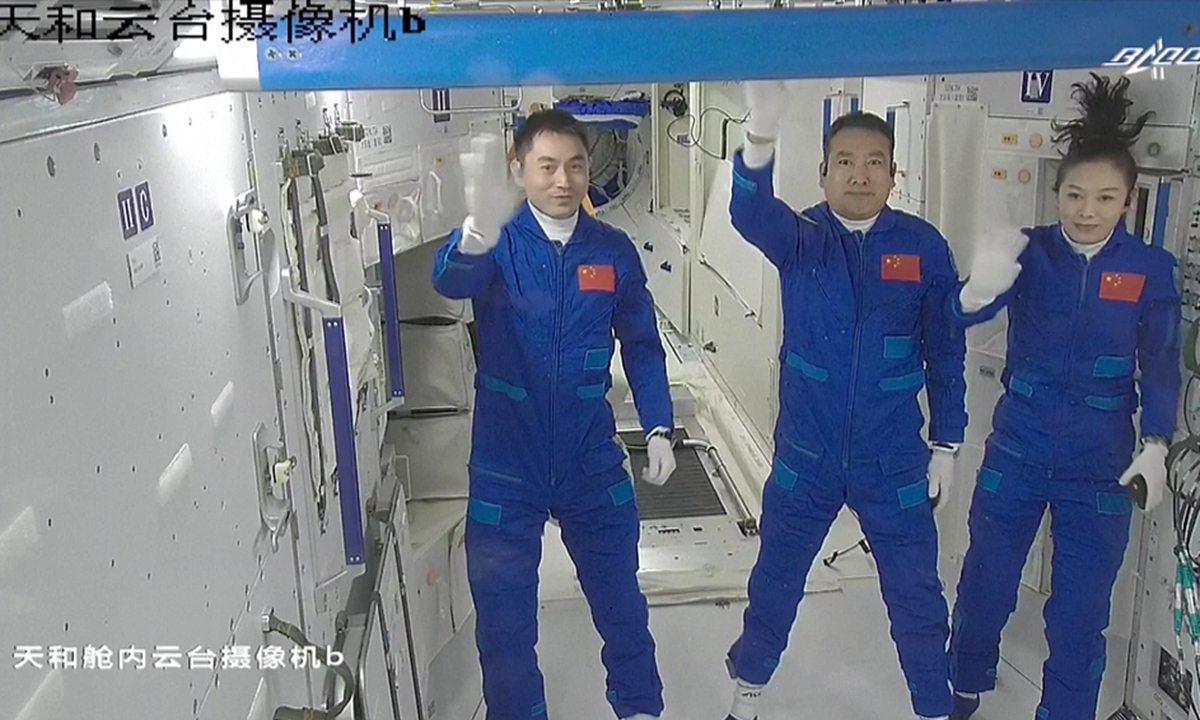
The Shenzhou-14 crew members, Chen Dong (center), Liu Yang (right) and Cai Xuzhe salute from the Wentian (Quest to The Heavens) lab module on July 25, 2022 from some 400 kilometers above the Earth. The three taikonauts checked in to their office and home unit in space at 10:03 am. Photo: cnsphoto
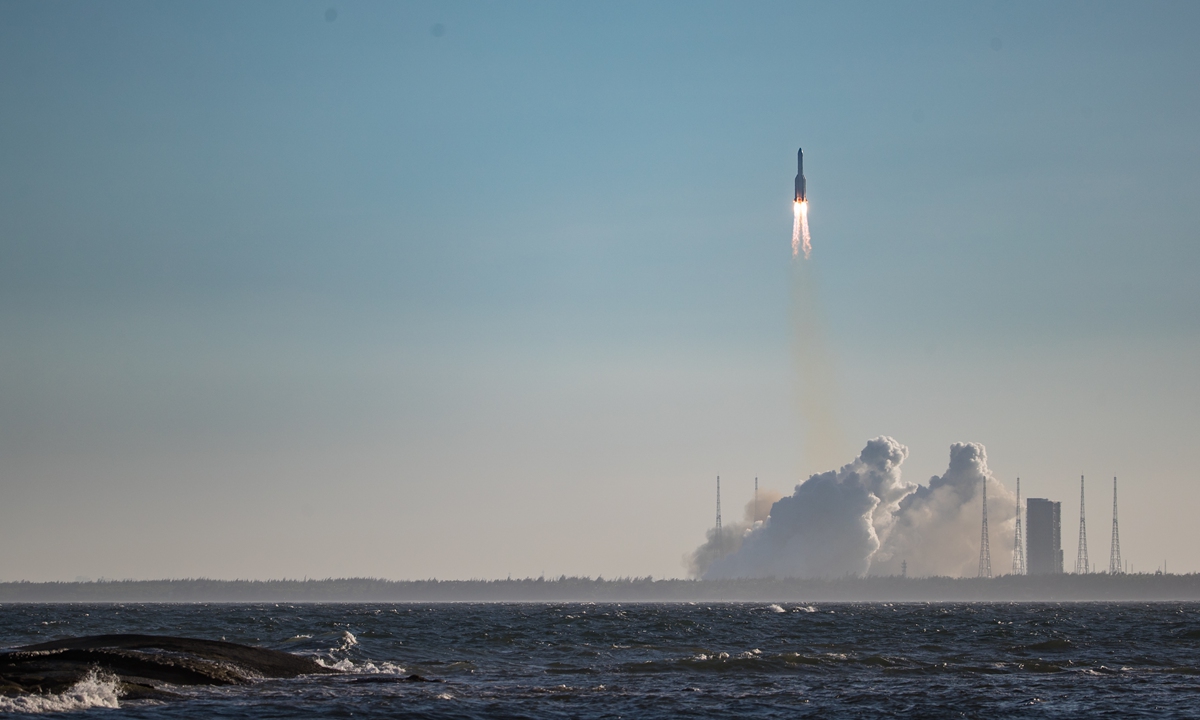
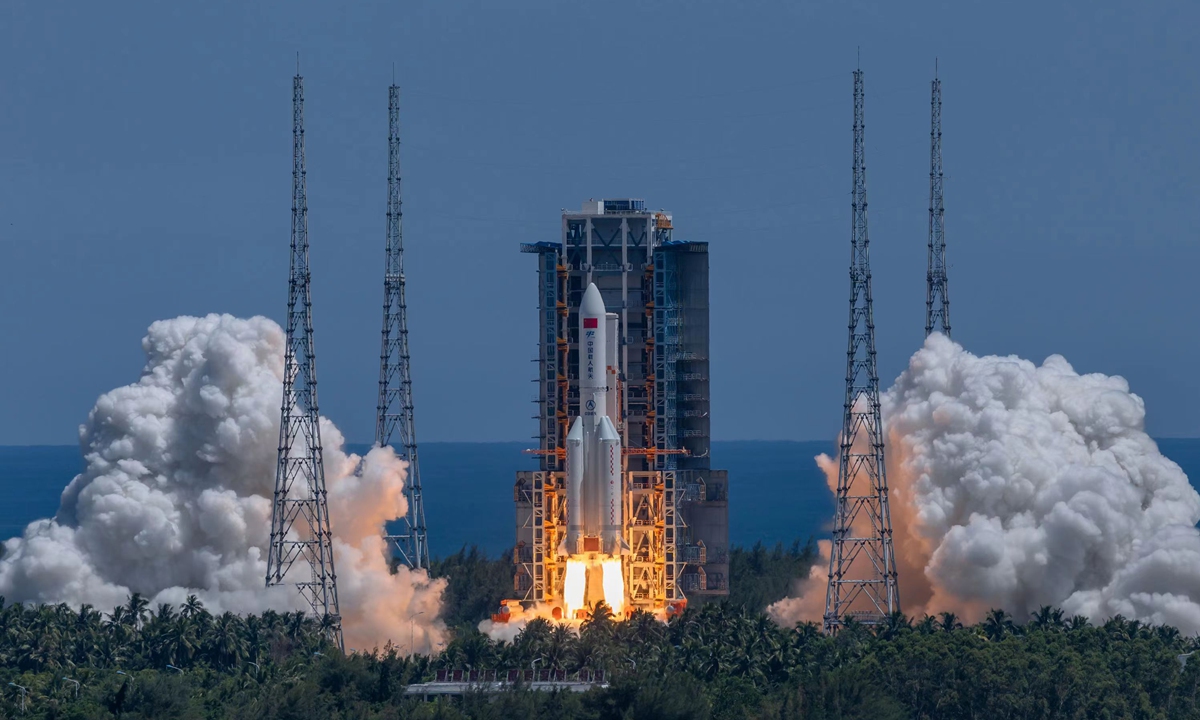
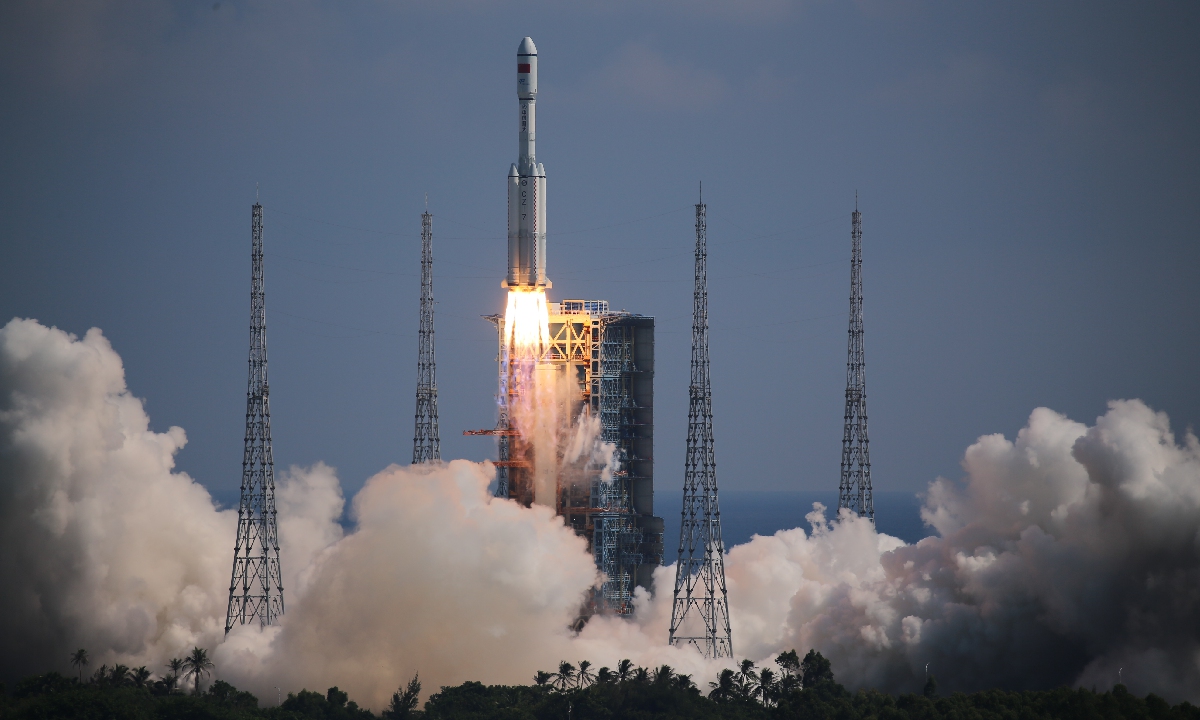
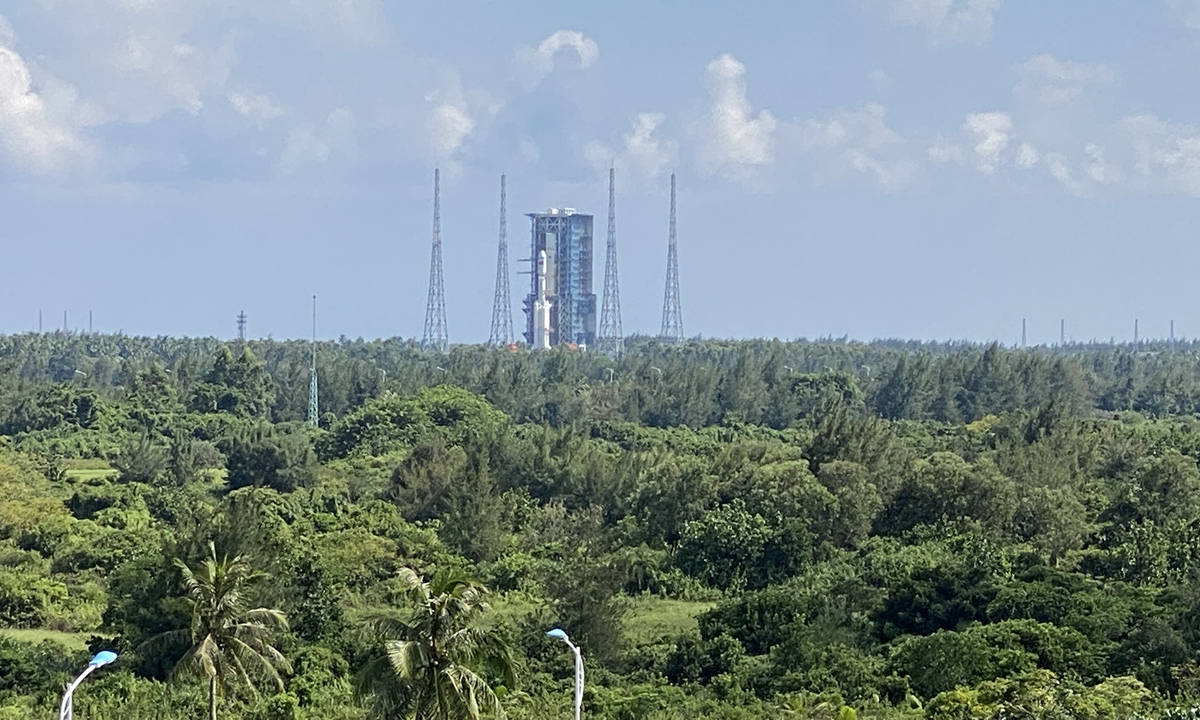
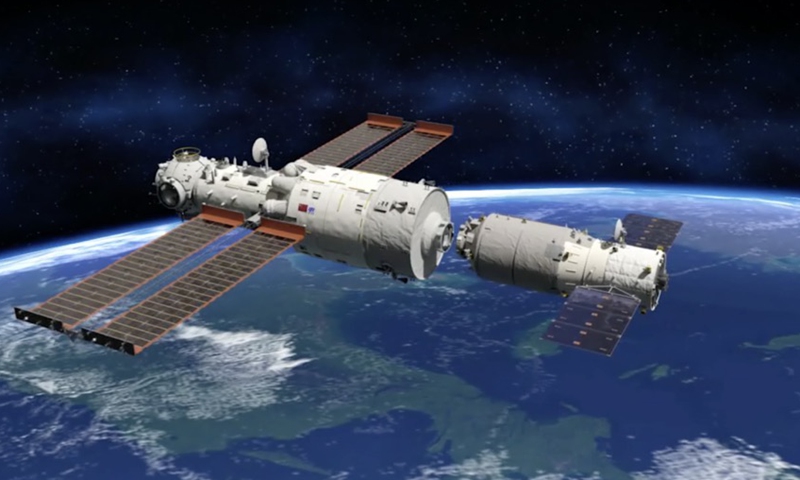
The Shenzhou-14 crew of three taikonauts, who watched live the epic launch of the Wentian [Quest to The Heavens] lab module from some 400 kilometers above the Earth and cheered it on with applause on Sunday, did not wait long to check into their office and home unit in space, as they opened the gate of the freshly docked new module and entered the Wentian at 10:03 am on Monday, the Global Times learned from the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA). It was a historic first that the taikonauts entered the scientific lab module in orbit, the CMSA noted in a statement it provided to the Global Times on Monday morning, while disclosing that the crew shall execute missions including space station combination attitude control, verification of robotic arms, and use of the Wentian airlock and its small robotic arm to perform spacewalks under the plan. The Wentian lab module conducted a smooth rendezvous and docking with the China Space Station's Tianhe core module at the front port at 3:13 am on Monday, some 13 hours after it was launched via a giant Long March-5B carrier rocket from South China's tropical island province of Hainan. It was a first for two pieces of 20-ton level spacecraft to execute the "heavenly kiss" in the country's history, and it also marked an unprecedented milestone event that took place while the China Space Station combination was carrying taikonauts onboard, the CMSA announced. Before China, only the former Soviet Union and the US were capable of assembling ultra-large spacecraft in orbit. Designed mainly to support space science and biology experiments, the 23-ton Wentian lab module is heavier than any other single-module spacecraft currently in space, including those with the International Space Station (ISS), the Global Times learned from the mission contractor, the state-owned space giant China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp (CASC). The Wentian also hosts eight experimental cabinets onboard. It will mainly focus on the study of space life sciences, which can support the growth, development, genetics and aging of multiple species of plants, animals and microorganisms under space conditions, Lü Congmin, a research fellow at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and deputy chief designer of the space utilization system of China Manned Space programs, told the Global Times. More than 10 research directions have been planned and more than 40 scientific projects have been established for the Wentian, Lü said. To meet the high energy requirements for the large number of scientific experiments in space, the Wentian is equipped with a pair of the largest flexible solar panels that the country has ever developed.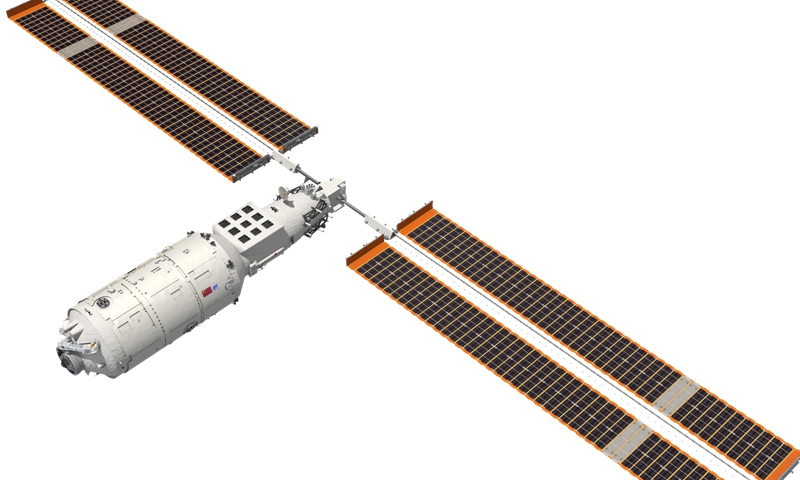
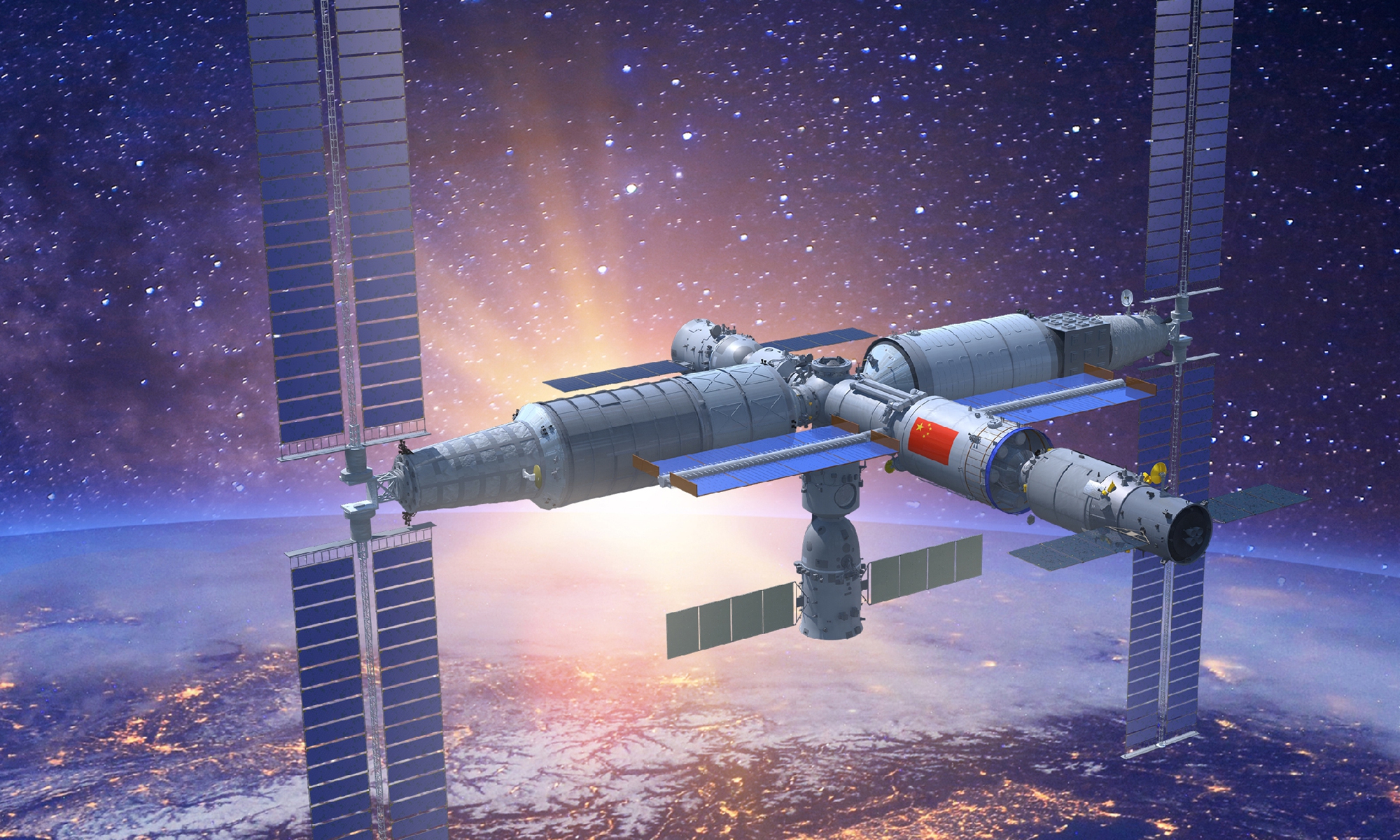
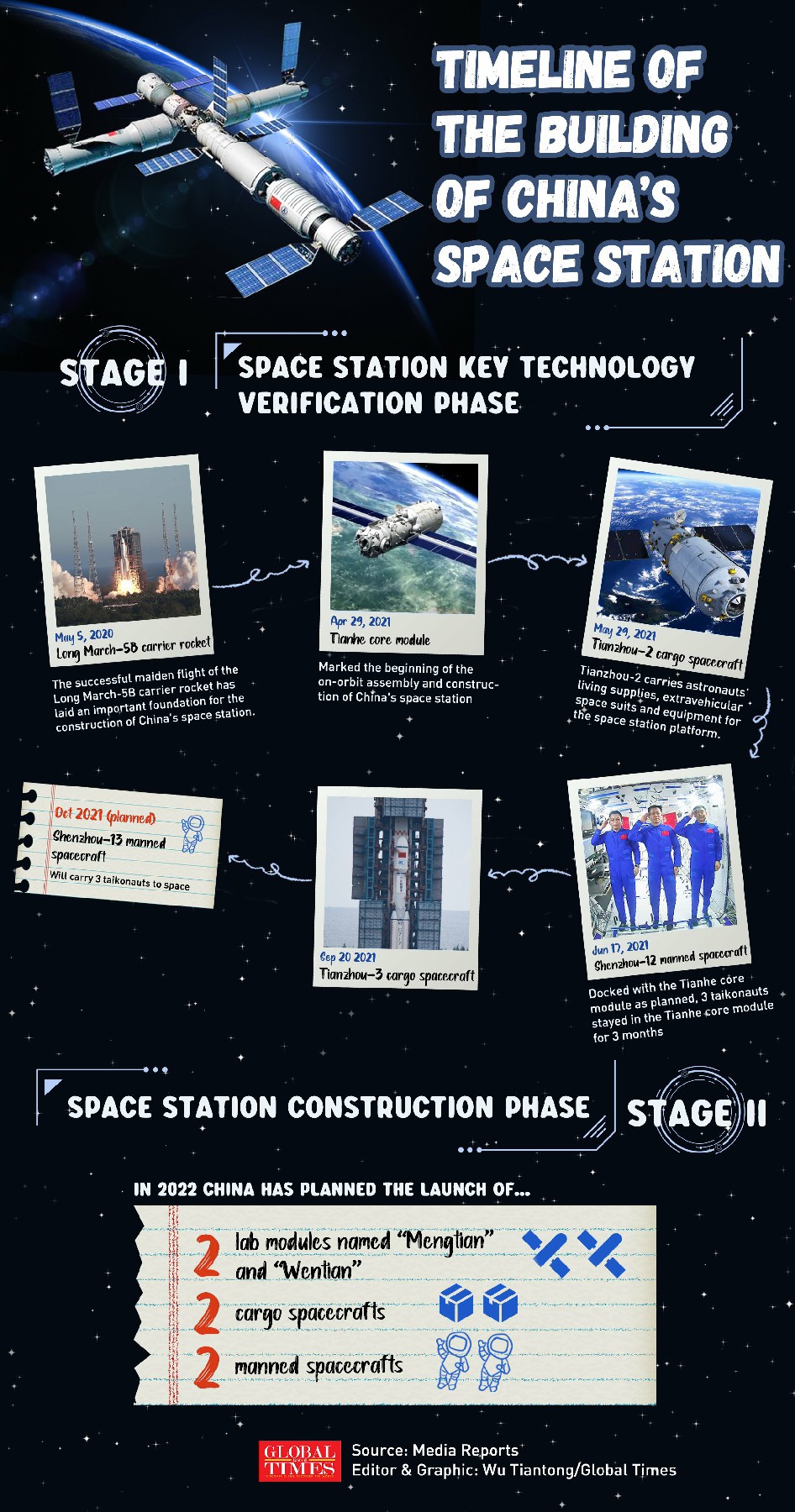
The China Space Station is planned to become fully operational before the end of 2022, aiming to accomplish the in-orbit assembly of the country's most ambitious program in less than one year and a half since the launch of the Tianhe core module in April 2021.
Related posts:
US versus China – in outer space
Tiangong-2 space lab draws global praise, with the world’s first “cold” atomic clock on board
China successfully launches 1st Mars probe
China unveils its 2020 Mars probe, Tianwen-1 天問一号
Chinese home in space
China launches 1st lunar sample return mission, aims for multiple breakthroughs in aerospace history
China's Chang'e-4 spacecraft, a world's first mission to moon's far side, boosts Beijing a space superpower
Long March-5 rocket in position for China's first Mars probe
China’s Zhurong sends back signals, marking success of Tianwen-1's landing on Mars
China lands on far side of the moon
Lunar probe, eliminating poverty, China did both












 Graphic: Chen Xia/GT
Graphic: Chen Xia/GT







 The Silicon Valley folklore is that of a lone maverick who has a great idea and pushes it to fruition, and in the process, creates a multibillion-dollar industry. That cannot be further from the assumption behind Japanese-Korean-Chinese state industrial policy, according to which innovation is a collective enterprise, not one of individual genius or charisma. It’s all about the sustained commitment of public resources and collective talent between the state and the private sector.
It’s a common criticism that such a policy is wasteful; it often backs the wrong technologies and industries. That’s true. However, the Silicon Valley model is also prone to periodic market euphoria, mania, panic and crashes, from the dotcom implosion to the current ongoing crypto-crashes. I will leave it to economic historians and econometricians to determine whether the state or non-state model is more wasteful or destructive.
Conclusions
Belatedly, the Biden administration is slowly realising that whether it’s containment against China or competition with it, the horse has bolted out of the barn already. That is why despite its hostile rhetoric, it has no coherent policy on how to deter or delay China’s technological drive for mastery or supremacy. This conflict cuts to the very ideological self-beliefs of the two countries. Only time will tell how it will turn out.
However, restricting or banning technological transfer will not work. The great British historian Arnold Toynbee famously wrote that it was usually countries or civilisations confronted with great or even mortal challenges that prevailed and prospered in history, not those that were well-endowed with rich resources. Denying China access to vital technologies at this late stage will simply force it to develop its own domestic capabilities. That won’t make it weaker, only stronger and more self-reliant.
For years, American policymakers and pundits have believed China’s search for technological mastery or supremacy is doomed to fail or at least be consigned forever to mediocrity and also-ran status. This belief lies behind the strategy, first put forward by the Donald Trump administration, and now followed by Joe Biden’s White House, to restrict or ban the transfer of crucial technologies, notably the most advanced semiconductors and their production methods.
And yet, paradoxically, China is bound to succeed, despite the inevitable hiccups and setbacks, because it is essentially replicating the actual history of the economics and policies that led the United States to technological dominance, rather than the ideological history of what many Americans believe lies behind their success.
The Silicon Valley folklore is that of a lone maverick who has a great idea and pushes it to fruition, and in the process, creates a multibillion-dollar industry. That cannot be further from the assumption behind Japanese-Korean-Chinese state industrial policy, according to which innovation is a collective enterprise, not one of individual genius or charisma. It’s all about the sustained commitment of public resources and collective talent between the state and the private sector.
It’s a common criticism that such a policy is wasteful; it often backs the wrong technologies and industries. That’s true. However, the Silicon Valley model is also prone to periodic market euphoria, mania, panic and crashes, from the dotcom implosion to the current ongoing crypto-crashes. I will leave it to economic historians and econometricians to determine whether the state or non-state model is more wasteful or destructive.
Conclusions
Belatedly, the Biden administration is slowly realising that whether it’s containment against China or competition with it, the horse has bolted out of the barn already. That is why despite its hostile rhetoric, it has no coherent policy on how to deter or delay China’s technological drive for mastery or supremacy. This conflict cuts to the very ideological self-beliefs of the two countries. Only time will tell how it will turn out.
However, restricting or banning technological transfer will not work. The great British historian Arnold Toynbee famously wrote that it was usually countries or civilisations confronted with great or even mortal challenges that prevailed and prospered in history, not those that were well-endowed with rich resources. Denying China access to vital technologies at this late stage will simply force it to develop its own domestic capabilities. That won’t make it weaker, only stronger and more self-reliant.
For years, American policymakers and pundits have believed China’s search for technological mastery or supremacy is doomed to fail or at least be consigned forever to mediocrity and also-ran status. This belief lies behind the strategy, first put forward by the Donald Trump administration, and now followed by Joe Biden’s White House, to restrict or ban the transfer of crucial technologies, notably the most advanced semiconductors and their production methods.
And yet, paradoxically, China is bound to succeed, despite the inevitable hiccups and setbacks, because it is essentially replicating the actual history of the economics and policies that led the United States to technological dominance, rather than the ideological history of what many Americans believe lies behind their success.
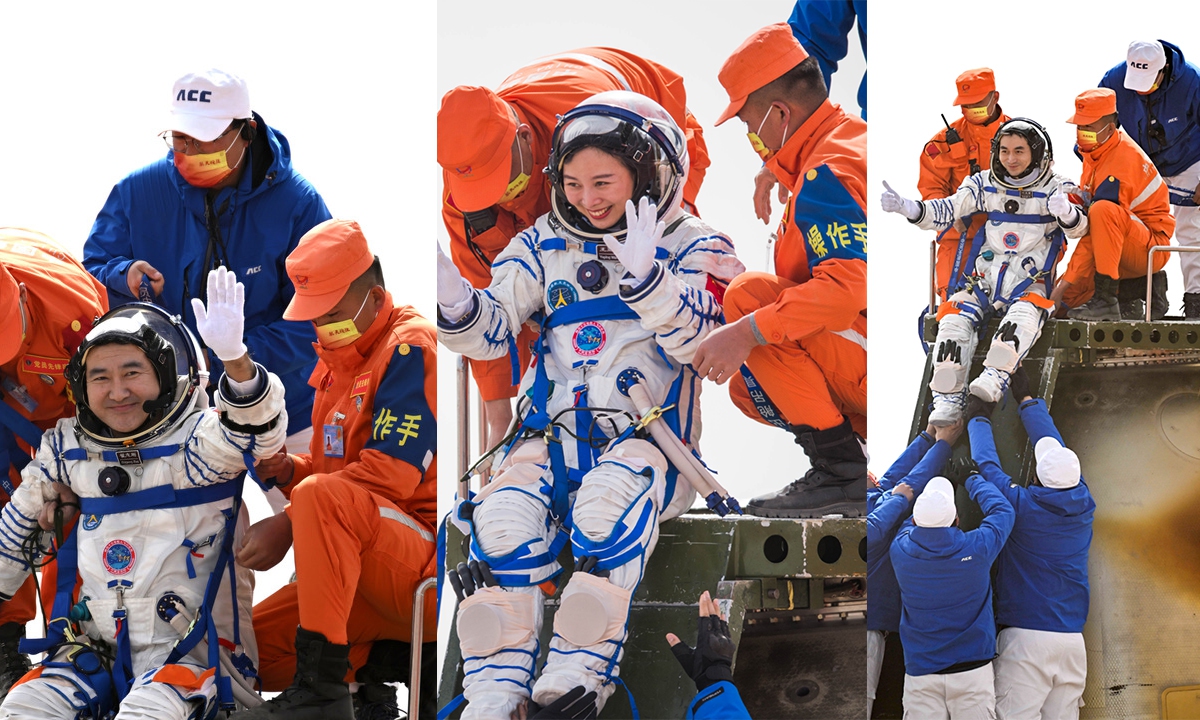


 Shenzhou-13 crew
Shenzhou-13 crew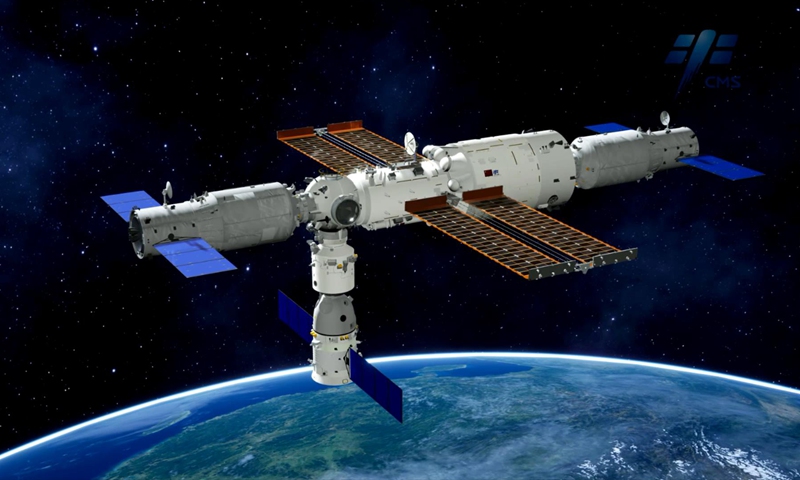

















 Nicolas Berggruen and Nathan Gardels are the founders of the Berggruen Institute and the authors of Intelligent Governance for the 21st Century: A Middle Way between West and East (2012). Their latest work, Renovating Democracy: Governing in the Age of Globalization and Digital Capitalism (2019), is the first in a Berggruen Institute series on the “
Nicolas Berggruen and Nathan Gardels are the founders of the Berggruen Institute and the authors of Intelligent Governance for the 21st Century: A Middle Way between West and East (2012). Their latest work, Renovating Democracy: Governing in the Age of Globalization and Digital Capitalism (2019), is the first in a Berggruen Institute series on the “



