.Covid-19 can affect our blood vessels, causing blood to clot more easily, which can result in stroke, heart attack or pulmonary embolism, among other conditions - AFP
HOW DOES COVID-19 AFFECT THE BODY?
https://youtu.be/Xj1nUFFVK1E
https://youtu.be/jXiG3FeBVko
Covid-19 can have a wide-ranging effect on many organs in our body
THE last time, you were telling me about many unusual Covid-19 symptoms, such as Covid toes, skin rashes. and loss of smell and taste (From taste to toes, StarHealth, May 31). What about the gut?
Yes. The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes Covid-19 binds to our lung cells using the cell’s ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) receptor.
This receptor is also present in our intestinal cells.
The theory is that the virus is in our saliva.
When we swallow our saliva, the virus gets into our guts and binds to our intestinal cells using their ACE2 receptors.
Once this happens, we get diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting.
Sometimes, a Covid-19 patient may only experience these symptoms, without any lung problems like a dry cough or difficulty breathing.
Covid-19 patients with gut problems tend to be diagnosed later and have longer infections.
On average, Covid-19 patients have diarrhoea for five days.
Wait, if Covid-19 patients have diarrhoea, does that mean we have to be careful about using toilets then?
Yes. For example, if one of your family members has Covid-19, it might be advisable to allocate one toilet for their use only, or at least allocate one toilet paper roll for their sole use.
You should also disinfect the toilet seat the patient is using after each use and wash your hands.
I have also heard of the kidney being affected?
You are right.
It occurs through the same mechanism; the kidney also carries ACE2 receptors on its cell membranes.
Some studies are finding that as much as one-third of Covid-19 patients admitted to hospital, develop kidney problems, resulting in acute renal (kidney) impairment, or worse, outright acute renal failure. Some patients even require dialysis.
Patients who develop kidney problems are usually the ones who also have the worst lung symptoms.
It may be that the amount of virus in them is very high and/or their immune system is acting up very badly.
When the immune system is heavily provoked, what happens is that it releases a cytokine storm.
The blood vessels are affected and they start to leak fluid.
When there is less fluid going into the kidneys, they do not get enough oxygen and their tubular cells get damaged.
Gosh! What are the other organs Covid-19 affects?
There is also the liver. Once again, this is an organ with cells rich in ACE2 receptors.b
Over half the patients hospitalised for Covid-19 develop some kind of liver impairment.
This is diagnosed by a blood test showing elevated liver enzymes.
Luckily, the liver is not usually affected so badly by Covid-19 that it results in acute liver failure.
The theory for this is that the kidneys may be directly affected by the virus, but the liver is not, and any ill effects on it are more a result of the body’s own cytokine storm.
I really think I don’t want to risk getting Covid-19! Are there any other organs affected?
You are wise. It really is not worth the risk as we can be one of those that are affected very badly.
As for your question, the brain is also affected.
The brain? How?
It has all to do with the ACE2 receptors again.
You see, many blood vessel cells also have these receptors.
As blood vessels are present all over our body, any effects on them are not restricted to a specific organ, like the lung, kidneys and intestines.
We are learning that immunity and gut health are intertwined.
Your digestive tract contains beneficial bacteria (probiotics) that you can increase in amount by eating fermented foods like yoghurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir and natto.
This may help strengthen your immune system by helping it to identify harmful microorganisms as a healthy ecosystem of gut bacteria teaches your immune system how to tell the difference between good bacteria and bad bacteria (pathogens that cause problems).
In a three-month study in 126 children, those who drank 70ml of fermented milk every day were found to have less childhood infectious diseases by about 20%, compared with a control group.
Another study of 152 people infected with a rhinovirus found that those who supplemented with the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis had a much better immune response and lower levels of the virus in their nasal mucus.
Cut your sugar intake
A high intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates contribute to obesity, heart disease and other conditions that disrupt your immune system.
According to an observational study in around 1,000 people, obese people who were administered the flu vaccine were twice as likely to still get the flu, compared to non-obese individuals who received the vaccine.
Curbing your sugar intake can decrease inflammation and aid weight loss, thus reducing your risk of chronic health conditions.
Strive to keep your added sugar intake to 5% or less of your daily calories, which is equal to about two tablespoons of sugar for a 2,000-calorie diet.
Throw in some exercise
Moderate exercise can give your immune system a boost.
Studies indicate that even a single session of moderate exercise can boost the effectiveness of vaccines in people with compromised immune systems.
By making it a regular routine, moderate exercise helps your immune cells to regenerate often and reduce inflammation.
Some types of exercises you can do include brisk walking, indoor cycling, jogging, swimming and hiking.
Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
Drink enough fluids
Dehydration paves the way to making your body susceptible to falling sick.
Without enough water, you may experience headaches and hinder your physical performance, focus, mood, digestion, and heart and kidney functions.
Hydration itself doesn’t protect you from germs and viruses, but dehydration increases your susceptibility to illness.
To know that you are drinking enough water regularly, the colour of your urine should be a clear, light yellow.
Plain water is the best option to stay hydrated – it is free of calories, additives and sugar.
You will need more fluids if you exercise a lot, work outside or if the weather is hot.
Keep stress at bay
Reducing anxiety and stress will help to improve immune health.
In the long run, stress increases inflammation and messes with your hormonal balance and immune cell function.
Long-term stress is especially taxing on children, weakening their immune response
Activities that are often recommended to help people manage stress include exercise, journaling, drawing or painting, meditation, outdoor walks and other mindfulness practices.
If you feel a need to express how you feel to someone, then seeing a certified counsellor or therapist can help.
Supplement wisely
;
Two things to note about supplements: the first is that they are not a replacement for a well-rounded diet, and the second is that they don’t guarantee that you will be free from getting sick.
Some studies however, have found that supplements may fight off viral infections, or at least give your immune system a helping hand in staying strong.
If you would like to take supplements, choose wisely.
Here are some vitamins and minerals to consider taking that may help improve your immunity:
This vitamin is vital to supporting biochemical reactions in the immune system.
Vitamin B6-rich foods include chicken, cold water fish such as salmon and tuna, green vegetables and chickpeas.
The bottom line is that improving your lifestyle and making better dietary choices can help strengthen your immune system to fight off harmful pathogens and keep you healthy and well.
 By Datuk Dr Nor Ashikin Mokhtar,
By Datuk Dr Nor Ashikin Mokhtar,
HOW DOES COVID-19 AFFECT THE BODY?
https://youtu.be/Xj1nUFFVK1E
https://youtu.be/jXiG3FeBVko
Health DG shares happy photos of Chinese couple who recovered from Covid-19
https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2020/02/18/health-dg-shares-happy-photos-of-chinese-couple-who-recovered-from-covid-19?jwsource=clAffecting multiple organs
Covid-19 can have a wide-ranging effect on many organs in our body
THE last time, you were telling me about many unusual Covid-19 symptoms, such as Covid toes, skin rashes. and loss of smell and taste (From taste to toes, StarHealth, May 31). What about the gut?
Yes. The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes Covid-19 binds to our lung cells using the cell’s ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) receptor.
This receptor is also present in our intestinal cells.
The theory is that the virus is in our saliva.
When we swallow our saliva, the virus gets into our guts and binds to our intestinal cells using their ACE2 receptors.
Once this happens, we get diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting.
Sometimes, a Covid-19 patient may only experience these symptoms, without any lung problems like a dry cough or difficulty breathing.
Covid-19 patients with gut problems tend to be diagnosed later and have longer infections.
On average, Covid-19 patients have diarrhoea for five days.
Wait, if Covid-19 patients have diarrhoea, does that mean we have to be careful about using toilets then?
Yes. For example, if one of your family members has Covid-19, it might be advisable to allocate one toilet for their use only, or at least allocate one toilet paper roll for their sole use.
You should also disinfect the toilet seat the patient is using after each use and wash your hands.
I have also heard of the kidney being affected?
You are right.
It occurs through the same mechanism; the kidney also carries ACE2 receptors on its cell membranes.
Some studies are finding that as much as one-third of Covid-19 patients admitted to hospital, develop kidney problems, resulting in acute renal (kidney) impairment, or worse, outright acute renal failure. Some patients even require dialysis.
Patients who develop kidney problems are usually the ones who also have the worst lung symptoms.
It may be that the amount of virus in them is very high and/or their immune system is acting up very badly.
When the immune system is heavily provoked, what happens is that it releases a cytokine storm.
The blood vessels are affected and they start to leak fluid.
When there is less fluid going into the kidneys, they do not get enough oxygen and their tubular cells get damaged.
Gosh! What are the other organs Covid-19 affects?
There is also the liver. Once again, this is an organ with cells rich in ACE2 receptors.b
Over half the patients hospitalised for Covid-19 develop some kind of liver impairment.
This is diagnosed by a blood test showing elevated liver enzymes.
Luckily, the liver is not usually affected so badly by Covid-19 that it results in acute liver failure.
The theory for this is that the kidneys may be directly affected by the virus, but the liver is not, and any ill effects on it are more a result of the body’s own cytokine storm.
I really think I don’t want to risk getting Covid-19! Are there any other organs affected?
You are wise. It really is not worth the risk as we can be one of those that are affected very badly.
As for your question, the brain is also affected.
The brain? How?
It has all to do with the ACE2 receptors again.
You see, many blood vessel cells also have these receptors.
As blood vessels are present all over our body, any effects on them are not restricted to a specific organ, like the lung, kidneys and intestines.
So if Covid-19 directly affects the blood vessels of a patient, they will cause blood clots more easily as they are damaged.
In autopsies done on deceased Covid-19 patients, blood clots are apparent throughout many organs in their bodies.
This suggests that many blood vessels and organs are affected by the disease.
Once you have blood clots, you may have complications like stroke where blood clots travel to the arteries of the brain and clog them up.
Doctors have also observed patients with dizziness, confusion, delirium, altered mental state and muscle weakness.
This has to do with the brain getting inflamed.
Wait, when blood clots form in blood vessels, not only a stroke can happen, right? This can also cause a heart attack.
True, blood clots can lead to a heart attack or a pulmonary embolism when a clot gets into your lungs
In fact, Accident and Emergency departments in some hospitals have received patients with heart attacks who turn out to have Covid-19 when they were tested.
Covid-19 can also attack the heart directly by inflaming the heart muscles.
This is known as myocarditis.
In autopsies done on deceased Covid-19 patients, blood clots are apparent throughout many organs in their bodies.
This suggests that many blood vessels and organs are affected by the disease.
Once you have blood clots, you may have complications like stroke where blood clots travel to the arteries of the brain and clog them up.
Doctors have also observed patients with dizziness, confusion, delirium, altered mental state and muscle weakness.
This has to do with the brain getting inflamed.
Wait, when blood clots form in blood vessels, not only a stroke can happen, right? This can also cause a heart attack.
True, blood clots can lead to a heart attack or a pulmonary embolism when a clot gets into your lungs
In fact, Accident and Emergency departments in some hospitals have received patients with heart attacks who turn out to have Covid-19 when they were tested.
Covid-19 can also attack the heart directly by inflaming the heart muscles.
This is known as myocarditis.
It can lead to chest pain, abnormal heart rhythms and heart failure.
There is also a condition called “happy hypoxia”.
This is when a Covid-19 patient has very low levels of oxygen as shown on the monitor, but appears to be breathing more or less normally.
Many doctors have theorised that this condition could be due to blood clotting in the lungs.
DR.Y.L.M
Here are nine ways to strengthen your body’s defence system against illnesses through healthy eating and daily habits.
There is also a condition called “happy hypoxia”.
This is when a Covid-19 patient has very low levels of oxygen as shown on the monitor, but appears to be breathing more or less normally.
Many doctors have theorised that this condition could be due to blood clotting in the lungs.
DR.Y.L.M
Dr YLM graduated as a medical doctor, and has been writing for many years on various subjects such as medicine, health, computers and entertainment. For further information, email starhealth@thestar.com.my. The information contained in this column is for general educational purposes only. Neither The Star nor the author gives any warranty on accuracy, completeness, functionality, usefulness or other assurances as to such information. The Star and the author disclaim all responsibility for any losses, damage to property or personal injury suffered directly or indirectly from reliance on such information
Read more:
Boosting immunity
Here are nine ways to strengthen your body’s defence system against illnesses through healthy eating and daily habits.
dehydration makes you more susceptible to
falling sick, so ensure that you fill up on fluids, especially if you
are outside under the hot sun.— Filepicb
LATELY, we’ve all been wondering if we are doing enough to keep our bodies strong and warding off illnesses.
One critical way to ensure that you have a fighting chance is to boost your immunity.
The immune system is made up of organs, cells, tissues and processes that fight against germs and toxins trying to enter our body.
You can bolster your immune system by making good lifestyle and food choices; and you’ll see results by being consistent.
Your body will feel healthier, you’ll have more energy and you’ll spend less time waiting to see the doctor for a common ailment.
It’s important to note, however, that no matter how strong an immune system is, you cannot stop bacteria and viruses from entering your body.
In order to avoid contracting a dangerous disease like Covid-19, you should still practise social distancing, wear a mask and wash your hands frequently.
So just to be clear, the tips below are not to protect specifically against Covid-19, but to help you boost your immune strength to fight off all types of infections.
Get the proper amount of sleep
Adults need an average of seven to eight hours of sleep every night.
Teens need eight to 10 hours, and younger children and infants up to 14 hours of sleep daily.
A lack of sleep or poor quality sleep has been linked to a higher frequency of falling sick, leading researchers to believe that sleep and immunity have close ties.
Also, sleeping for longer periods when sick, lets your immune system fight illnesses more effectively so that you heal faster.
In a study involving 164 healthy adults, those who had less than six hours of sleep per night were more susceptible to colds, compared to those who had at least six hours of sleep.
To avoid having trouble falling asleep, there are several things you can do:
> Keep your room completely dark, e.g. close the curtains fully, remove any night lights or use a sleep mask.
> Keep your bed time consistent, even during weekends and holidays.
> Exercise regularly, even if it’s just brisk walking for 20 mins a day.
One critical way to ensure that you have a fighting chance is to boost your immunity.
The immune system is made up of organs, cells, tissues and processes that fight against germs and toxins trying to enter our body.
You can bolster your immune system by making good lifestyle and food choices; and you’ll see results by being consistent.
Your body will feel healthier, you’ll have more energy and you’ll spend less time waiting to see the doctor for a common ailment.
It’s important to note, however, that no matter how strong an immune system is, you cannot stop bacteria and viruses from entering your body.
In order to avoid contracting a dangerous disease like Covid-19, you should still practise social distancing, wear a mask and wash your hands frequently.
So just to be clear, the tips below are not to protect specifically against Covid-19, but to help you boost your immune strength to fight off all types of infections.
Get the proper amount of sleep
Adults need an average of seven to eight hours of sleep every night.
Teens need eight to 10 hours, and younger children and infants up to 14 hours of sleep daily.
A lack of sleep or poor quality sleep has been linked to a higher frequency of falling sick, leading researchers to believe that sleep and immunity have close ties.
Also, sleeping for longer periods when sick, lets your immune system fight illnesses more effectively so that you heal faster.
In a study involving 164 healthy adults, those who had less than six hours of sleep per night were more susceptible to colds, compared to those who had at least six hours of sleep.
To avoid having trouble falling asleep, there are several things you can do:
> Keep your room completely dark, e.g. close the curtains fully, remove any night lights or use a sleep mask.
> Keep your bed time consistent, even during weekends and holidays.
> Exercise regularly, even if it’s just brisk walking for 20 mins a day.
> Limit screen time (TV, phone,
laptop) at least an hour before bed in order to prevent the impact of
blue light from disrupting your circadian rhythm (your body’s natural
wake-sleep cycle).
Eat lots of whole plant foods
Whole plant foods like vegetables, nuts, seeds and fruit are rich in antioxidants, vitamin C and fibre.
Eating more of these nutrientdense foods helps to lower your risk of infections.
This is because the antioxidants in the foods decrease inflammation by battling unstable compounds known as free radicals.
Chronic inflammation has been found to occur more frequently in patients with heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and certain cancers, so it’s important to find effective ways to reduce inflammation.
At the same time, whole plant foods are high in fibre and feed your gut microbiome (the community of healthy bacteria in your gut).
A robust gut microbiome can improve your immunity and help keep harmful pathogens from entering your body via your digestive tract.
Additionally, other nutrients found in whole plant foods, like vitamin C, may help to reduce symptoms of the common cold.
Eat foods like papaya, broccoli, spinach, garlic, ginger, bell peppers and kiwi fruit.
Consume healthy fats
Eat lots of whole plant foods
Whole plant foods like vegetables, nuts, seeds and fruit are rich in antioxidants, vitamin C and fibre.
Eating more of these nutrientdense foods helps to lower your risk of infections.
This is because the antioxidants in the foods decrease inflammation by battling unstable compounds known as free radicals.
Chronic inflammation has been found to occur more frequently in patients with heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and certain cancers, so it’s important to find effective ways to reduce inflammation.
At the same time, whole plant foods are high in fibre and feed your gut microbiome (the community of healthy bacteria in your gut).
A robust gut microbiome can improve your immunity and help keep harmful pathogens from entering your body via your digestive tract.
Additionally, other nutrients found in whole plant foods, like vitamin C, may help to reduce symptoms of the common cold.
Eat foods like papaya, broccoli, spinach, garlic, ginger, bell peppers and kiwi fruit.
Consume healthy fats
Healthy omega-3 fats have anti-inflammatory properties.
These fats could be a key weapon in fighting against illnesses, considering that chronic inflammation prevents your immune system from performing at its best.
Healthy fats can be found in foods such as olive oil, salmon, chia seeds, sunflower seeds and almonds.
Olive oil, in particular, is highly anti-inflammatory, and has been known to decrease the risk of chronic problems like heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The anti-inflammatory properties of these healthy fats may be critical to helping your body fight off harmful disease-causing bacteria and viruses, so try to get more of it in your diet now.
Have more fermented foods
These fats could be a key weapon in fighting against illnesses, considering that chronic inflammation prevents your immune system from performing at its best.
Healthy fats can be found in foods such as olive oil, salmon, chia seeds, sunflower seeds and almonds.
Olive oil, in particular, is highly anti-inflammatory, and has been known to decrease the risk of chronic problems like heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The anti-inflammatory properties of these healthy fats may be critical to helping your body fight off harmful disease-causing bacteria and viruses, so try to get more of it in your diet now.
Have more fermented foods
We are learning that immunity and gut health are intertwined.
Your digestive tract contains beneficial bacteria (probiotics) that you can increase in amount by eating fermented foods like yoghurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir and natto.
This may help strengthen your immune system by helping it to identify harmful microorganisms as a healthy ecosystem of gut bacteria teaches your immune system how to tell the difference between good bacteria and bad bacteria (pathogens that cause problems).
In a three-month study in 126 children, those who drank 70ml of fermented milk every day were found to have less childhood infectious diseases by about 20%, compared with a control group.
Another study of 152 people infected with a rhinovirus found that those who supplemented with the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis had a much better immune response and lower levels of the virus in their nasal mucus.
Cut your sugar intake
A high intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates contribute to obesity, heart disease and other conditions that disrupt your immune system.
According to an observational study in around 1,000 people, obese people who were administered the flu vaccine were twice as likely to still get the flu, compared to non-obese individuals who received the vaccine.
Curbing your sugar intake can decrease inflammation and aid weight loss, thus reducing your risk of chronic health conditions.
Strive to keep your added sugar intake to 5% or less of your daily calories, which is equal to about two tablespoons of sugar for a 2,000-calorie diet.
Throw in some exercise
Moderate exercise can give your immune system a boost.
Studies indicate that even a single session of moderate exercise can boost the effectiveness of vaccines in people with compromised immune systems.
By making it a regular routine, moderate exercise helps your immune cells to regenerate often and reduce inflammation.
Some types of exercises you can do include brisk walking, indoor cycling, jogging, swimming and hiking.
Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
Drink enough fluids
Dehydration paves the way to making your body susceptible to falling sick.
Without enough water, you may experience headaches and hinder your physical performance, focus, mood, digestion, and heart and kidney functions.
Hydration itself doesn’t protect you from germs and viruses, but dehydration increases your susceptibility to illness.
To know that you are drinking enough water regularly, the colour of your urine should be a clear, light yellow.
Plain water is the best option to stay hydrated – it is free of calories, additives and sugar.
You will need more fluids if you exercise a lot, work outside or if the weather is hot.
Keep stress at bay
Reducing anxiety and stress will help to improve immune health.
In the long run, stress increases inflammation and messes with your hormonal balance and immune cell function.
Long-term stress is especially taxing on children, weakening their immune response
Activities that are often recommended to help people manage stress include exercise, journaling, drawing or painting, meditation, outdoor walks and other mindfulness practices.
If you feel a need to express how you feel to someone, then seeing a certified counsellor or therapist can help.
Supplement wisely
;
Two things to note about supplements: the first is that they are not a replacement for a well-rounded diet, and the second is that they don’t guarantee that you will be free from getting sick.
Some studies however, have found that supplements may fight off viral infections, or at least give your immune system a helping hand in staying strong.
If you would like to take supplements, choose wisely.
Here are some vitamins and minerals to consider taking that may help improve your immunity:
> Vitamin E
This vitamin is a powerful antioxidant that helps the body fight off infection, and is found in foods like nuts, seeds and spinach.
> Zinc
A peer review of 575 people with the common cold, who took more than 75 mg of zinc per day, reduced the duration of their cold by one-third, compared to those who didn’t take the supplement.
This vitamin is a powerful antioxidant that helps the body fight off infection, and is found in foods like nuts, seeds and spinach.
> Zinc
A peer review of 575 people with the common cold, who took more than 75 mg of zinc per day, reduced the duration of their cold by one-third, compared to those who didn’t take the supplement.
> Vitamin D
A deficiency in this vitamin may increase your chances of getting sick, so supplementing may counteract this effect.
> Vitamin B6
This vitamin is vital to supporting biochemical reactions in the immune system.
Vitamin B6-rich foods include chicken, cold water fish such as salmon and tuna, green vegetables and chickpeas.
The bottom line is that improving your lifestyle and making better dietary choices can help strengthen your immune system to fight off harmful pathogens and keep you healthy and well.
who is a consultant obstetrician and
gynaecologist, and a functional medicine practitioner. For further
information, email starhealth@thestar.com.my. The information provided
is for educational and communication purposes only and it should not be
construed as personal medical advice. Information published in this
article is not intended to replace, supplant or augment a consultation
with a health professional regarding the reader’s own medical care. The
Star does not give any warranty on accuracy, completeness,
functionality, usefulness or other assurances as to the content
appearing in this column. The Star disclaims all responsibility for any
losses, damage to property or personal injury suffered directly or
indirectly from reliance
on such information
When muscles shrink
Despite having normal nutrition, many senior citizens actually have low muscle mass, making them more prone to falls and fractures.
MUSCLE loss or sarcopenia is a natural part of ageing and one of the main contributors to musculoskeletal impairments in the elderly.
MUSCLE loss or sarcopenia is a natural part of ageing and one of the main contributors to musculoskeletal impairments in the elderly.
Strong muscles support the joints as they help absorb the stress placed on the joints when you move.
Without adequate muscles, the joints take a beating, and can cause the individual to become frail and more likely to suffer from falls and fractures.
The 2018 Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) reported that 15% of those aged above 60 had fallen at least once over 12 months.
Half suffered injuries, while one in five were hospitalised.
Even if you are active, it is still possible to have some muscle loss beginning in your 30s.
However, there are steps you can take to slow down or prevent losing muscle.
Missing muscles
According to Asia’s largest clinical study of its kind on nutritional outcomes in the elderly, there was a prevalence of low muscle mass among the elderly, despite them being active, healthy and without any chronic medical illnesses.
The two-part Singaporean study, called Strengthening Health in Elderly through Nutrition (Shield), was jointly carried out by Changi General Hospital (CGH), Sing Health Polyclinics and healthcare company Abbott.
Without adequate muscles, the joints take a beating, and can cause the individual to become frail and more likely to suffer from falls and fractures.
The 2018 Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) reported that 15% of those aged above 60 had fallen at least once over 12 months.
Half suffered injuries, while one in five were hospitalised.
Even if you are active, it is still possible to have some muscle loss beginning in your 30s.
However, there are steps you can take to slow down or prevent losing muscle.
Missing muscles
According to Asia’s largest clinical study of its kind on nutritional outcomes in the elderly, there was a prevalence of low muscle mass among the elderly, despite them being active, healthy and without any chronic medical illnesses.
The two-part Singaporean study, called Strengthening Health in Elderly through Nutrition (Shield), was jointly carried out by Changi General Hospital (CGH), Sing Health Polyclinics and healthcare company Abbott.
Results from the first phase of the study was published in the Plos One journal last year.
This observational phase looked at 400 healthy individuals in Singapore aged 65 and older.
The results revealed that the prevalence of low muscle mass was higher in females (24.9%) than in males (15.5%), with even adults with normal nutritional status at risk for having lower muscle mass. (See Maintaining muscles during menopause).
Every one-year increase in age over 65 years was associated with 13% higher odds of having low muscle mass.
And 52% of participants had vitamin D insufficiency despite living on an island where sunshine is available the whole year round.
“The majority (93%) of the subjects were fully independent and self-caring in the community.
“All the subjects were living at home and able to walk independently without any walking aids, and were relatively active prior to the study
“Participants were not subjected to any exercise programmes before or during the study.
“We assessed their physical activity level using the PASE (Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly) questionnaire.
“The average PASE score of the study participants was 119.45, similar to the norm of older adults,” says principal investigator Dr Samuel Chew, adjunct associate professor and senior consultant at the geriatric medicine department at CGH.
However, the subjects’ daily diet was not collected in this first part of the study.
A combination of physical activity, which includes weights or resistance training, and a balanced diet with an adequate amount of high-quality protein (e.g. chicken breast, fish, eggs, tofu and other soya products), is essential for good muscle health and function.
However, many seniors don’t embark on strength training programmes and cite difficulty in chewing meats and poultry due to deteriorating teeth, so they avoid eating protein or get little of it in their diets.
Assoc Prof Chew says, “We are unable to comment on the possible reasons for the observed low muscle mass, but from the available literature, there is a measurable decline in muscle mass from the age of 40.
“The decline rate increases by about 8% every 10 years and accelerates after the age of 70 to about 15% every 10 years.
“There are many factors that contribute to this loss in muscle mass, such as changes in hormone and endocrine levels, the loss of connections between the nerves and muscle units with the onset of ageing, acute or chronic illness, and inactivity.
“In addition, those above the age of 65 require more dietary protein in order to stimulate the same amount of muscle protein synthesis as a young person.”
Other factors that may impact elderly diets are:
> The lack of knowledge about good nutrition
> The lack of awareness about the high prevalence of low muscle mass and inadequate levels of micronutrients such as vitamin D
And 52% of participants had vitamin D insufficiency despite living on an island where sunshine is available the whole year round.
“The majority (93%) of the subjects were fully independent and self-caring in the community.
“All the subjects were living at home and able to walk independently without any walking aids, and were relatively active prior to the study
“Participants were not subjected to any exercise programmes before or during the study.
“We assessed their physical activity level using the PASE (Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly) questionnaire.
“The average PASE score of the study participants was 119.45, similar to the norm of older adults,” says principal investigator Dr Samuel Chew, adjunct associate professor and senior consultant at the geriatric medicine department at CGH.
However, the subjects’ daily diet was not collected in this first part of the study.
A combination of physical activity, which includes weights or resistance training, and a balanced diet with an adequate amount of high-quality protein (e.g. chicken breast, fish, eggs, tofu and other soya products), is essential for good muscle health and function.
However, many seniors don’t embark on strength training programmes and cite difficulty in chewing meats and poultry due to deteriorating teeth, so they avoid eating protein or get little of it in their diets.
Assoc Prof Chew says, “We are unable to comment on the possible reasons for the observed low muscle mass, but from the available literature, there is a measurable decline in muscle mass from the age of 40.
“The decline rate increases by about 8% every 10 years and accelerates after the age of 70 to about 15% every 10 years.
“There are many factors that contribute to this loss in muscle mass, such as changes in hormone and endocrine levels, the loss of connections between the nerves and muscle units with the onset of ageing, acute or chronic illness, and inactivity.
“In addition, those above the age of 65 require more dietary protein in order to stimulate the same amount of muscle protein synthesis as a young person.”
Other factors that may impact elderly diets are:
> The lack of knowledge about good nutrition
> The lack of awareness about the high prevalence of low muscle mass and inadequate levels of micronutrients such as vitamin D
> Poor oral health
> Loss of appetite due to physiological and sensory/taste changes associated with ageing
> Living alone
> Other illnesses
> Use of multiple medications
Get some sunshine
As for the lack of vitamin D, it is apparently common in older adults.
“The results from our study are consistent with previous studies performed in Asia.
“Therefore, while the finding is not unexpected, it still poses a cause for concern.
“Vitamin D is produced in the body naturally when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
“It is also found in dietary sources such as dairy products, oily fish, eggs and mushrooms.
“As such, it is likely that the vitamin D insufficiency is related to a lack of exposure to sunlight and/or insufficient intake of vitamin D-rich food sources,” explains Assoc Prof Chew.
To overcome this deficiency, one method is to get 15 minutes of exposure to outdoor sunlight daily.
He asserts, “It is vital for the activity to take place outdoors, as the component of sunlight that stimulates the production of vitamin D in the human skin does not penetrate glass windows very well.
“However, be mindful of direct overexposure to sunlight, which may result in skin damage and other health complications.”
The Shield study compares to a similar European ageing study that was carried out in Berlin, Germany, where the prevalence of sarcopenia was 24.3%.
“Many factors can affect the results, such as the characteristics of the study participants, methods used to measure muscle mass and cut-off criteria used to define low muscle mass, and participants’ nutritional status.
“The study conducted in Europe included generally healthy community-dwelling older adults who may have had normal nutritional status or were at risk of malnutrition, which is a risk factor for low muscle mass.
“Therefore, the true prevalence of low muscle mass in the general population aged 65 years and above in Singapore is likely going to be higher than the prevalence observed in our study, as they would include individuals who are at risk of malnutrition,” says study co-investigator and Abbott Scientific & Medical Affairs divisional vice-president Dr Low Yen Ling.
While no similar studies have been carried out in Malaysia, it is believed that our elderly could also be having low muscle mass.
Statistics from the Global Burden Disease Study 2010 shows that the lifespan of Singaporean men is 78.8 years, and for women, 83.3 years. So, even with lower muscle mass, women are living longer.
Dr Low reflects: “Biological, behavioural, and environmental factors can all contribute to this topic.
“One possible explanation is that men smoke more often than women.
“Some evidence also suggests that although both men and women are living longer as the burden of infectious diseases falls, such reduction may disproportionally benefit women.
“This is an ongoing effort and researchers are still studying how all these potential factors influence life expectancy and ways to improve longevity.
“What we know is that scientific evidence has shown that low muscle mass is associated with negative outcomes such as higher risk of functional impairment, fractures, complications, and even mortality.”
Less muscles, poorer immunity
Skeletal muscle accounts for about 40% of total body weight and contains at least half of all body proteins.
Data suggests that loss of muscle mass is associated with compromised immunity and infections.
Research in older adults has shown increased markers of inflammation associated with low muscle mass and muscle function.
Immunity is affected if an older adult loses more than 10% of their lean body mass, while a decrease of more than 30% can make them susceptible to pneumonia.
This is probably because muscles produce and release compounds that play an important role in the proliferation, activation and distribution of certain immune cells.
Assoc Prof Chew says, “Hospitalised patients with pneumonia may have poor outcomes, and this is often associated with very low muscle mass and poor nutrition – two factors that are also linked to a weakened immune system.
This is because muscles are a natural reservoir of amino acids, which are required for proper functioning of the immune system.
“Decreased muscle mass, together with the associated loss of physical strength and function, can lead to an impaired recovery from critical illness.
“Infection in an individual with deficient muscle mass causes further inflammation in the body, which can cause further loss of muscle mass and impairment of the immune system, resulting in a vicious cycle that may ultimately result in poor health outcomes.”
To help preserve muscles, Dr Low provides these tips:
> Engage in regular exercise
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderateintensity exercise a week, and include resistance training to maintain muscles and strength.
> Eat enough protein
Incorporate chicken, seafood, eggs, beans or dairy into your diet, and aim for about 20-30g per meal.
Adults 65 years and above may need up to 50% more protein than younger adults.
To further amp up protein intake, snack on proteins between meals or supplement your diet if needed with protein powders or shakes.
> Follow a balanced diet
Choose a balanced diet full of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, proteins, healthy fats, and key vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D.
> Consider HMB (beta-hydroxy-betamethylbutyrate)
HMB is a metabolite of the essential amino acid leucine and a naturally-occurring compound that has been shown to preserve muscle mass in healthy older adults when taken as a supplement.
While HMB is naturally found in very small amounts in foods such as avocados, grapefruit and catfish, it’s hard to get enough from food sources alone to achieve the desired health benefits.
Having healthy muscles is critical to ensure that the elderly can continue to retain their mobility, strength, energy levels and independence as they age – the Shield study reinforces that.
There is also a correlation between skeletal muscle and bone health – healthy muscles link to healthy bones, but strong bones do not necessarily mean that the muscles are strong.
Dr Low suggests: “It is important to perform early screening to identify those who have low muscle mass, so that appropriate interventions can be implemented.
“Muscle health can be determined by using a handheld dynamometer (to test hand grip), measuring calf circumference or measuring muscle mass using the bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA).”
The second phase 2 of the Shield study, to be completed this year, will involve 800 elderly participants at risk of being malnourished, who will be placed on oral nutritional supplements.
> Loss of appetite due to physiological and sensory/taste changes associated with ageing
> Living alone
> Other illnesses
> Use of multiple medications
Get some sunshine
As for the lack of vitamin D, it is apparently common in older adults.
“The results from our study are consistent with previous studies performed in Asia.
“Therefore, while the finding is not unexpected, it still poses a cause for concern.
“Vitamin D is produced in the body naturally when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
“It is also found in dietary sources such as dairy products, oily fish, eggs and mushrooms.
“As such, it is likely that the vitamin D insufficiency is related to a lack of exposure to sunlight and/or insufficient intake of vitamin D-rich food sources,” explains Assoc Prof Chew.
To overcome this deficiency, one method is to get 15 minutes of exposure to outdoor sunlight daily.
He asserts, “It is vital for the activity to take place outdoors, as the component of sunlight that stimulates the production of vitamin D in the human skin does not penetrate glass windows very well.
“However, be mindful of direct overexposure to sunlight, which may result in skin damage and other health complications.”
The Shield study compares to a similar European ageing study that was carried out in Berlin, Germany, where the prevalence of sarcopenia was 24.3%.
“Many factors can affect the results, such as the characteristics of the study participants, methods used to measure muscle mass and cut-off criteria used to define low muscle mass, and participants’ nutritional status.
“The study conducted in Europe included generally healthy community-dwelling older adults who may have had normal nutritional status or were at risk of malnutrition, which is a risk factor for low muscle mass.
“Therefore, the true prevalence of low muscle mass in the general population aged 65 years and above in Singapore is likely going to be higher than the prevalence observed in our study, as they would include individuals who are at risk of malnutrition,” says study co-investigator and Abbott Scientific & Medical Affairs divisional vice-president Dr Low Yen Ling.
Statistics from the Global Burden Disease Study 2010 shows that the lifespan of Singaporean men is 78.8 years, and for women, 83.3 years. So, even with lower muscle mass, women are living longer.
Dr Low reflects: “Biological, behavioural, and environmental factors can all contribute to this topic.
“One possible explanation is that men smoke more often than women.
“Some evidence also suggests that although both men and women are living longer as the burden of infectious diseases falls, such reduction may disproportionally benefit women.
“This is an ongoing effort and researchers are still studying how all these potential factors influence life expectancy and ways to improve longevity.
“What we know is that scientific evidence has shown that low muscle mass is associated with negative outcomes such as higher risk of functional impairment, fractures, complications, and even mortality.”
Less muscles, poorer immunity
Skeletal muscle accounts for about 40% of total body weight and contains at least half of all body proteins.
Data suggests that loss of muscle mass is associated with compromised immunity and infections.
Research in older adults has shown increased markers of inflammation associated with low muscle mass and muscle function.
Immunity is affected if an older adult loses more than 10% of their lean body mass, while a decrease of more than 30% can make them susceptible to pneumonia.
This is probably because muscles produce and release compounds that play an important role in the proliferation, activation and distribution of certain immune cells.
Assoc Prof Chew says, “Hospitalised patients with pneumonia may have poor outcomes, and this is often associated with very low muscle mass and poor nutrition – two factors that are also linked to a weakened immune system.
This is because muscles are a natural reservoir of amino acids, which are required for proper functioning of the immune system.
“Decreased muscle mass, together with the associated loss of physical strength and function, can lead to an impaired recovery from critical illness.
“Infection in an individual with deficient muscle mass causes further inflammation in the body, which can cause further loss of muscle mass and impairment of the immune system, resulting in a vicious cycle that may ultimately result in poor health outcomes.”
To help preserve muscles, Dr Low provides these tips:
> Engage in regular exercise
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderateintensity exercise a week, and include resistance training to maintain muscles and strength.
> Eat enough protein
Incorporate chicken, seafood, eggs, beans or dairy into your diet, and aim for about 20-30g per meal.
Adults 65 years and above may need up to 50% more protein than younger adults.
To further amp up protein intake, snack on proteins between meals or supplement your diet if needed with protein powders or shakes.
> Follow a balanced diet
Choose a balanced diet full of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, proteins, healthy fats, and key vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D.
> Consider HMB (beta-hydroxy-betamethylbutyrate)
HMB is a metabolite of the essential amino acid leucine and a naturally-occurring compound that has been shown to preserve muscle mass in healthy older adults when taken as a supplement.
While HMB is naturally found in very small amounts in foods such as avocados, grapefruit and catfish, it’s hard to get enough from food sources alone to achieve the desired health benefits.
Having healthy muscles is critical to ensure that the elderly can continue to retain their mobility, strength, energy levels and independence as they age – the Shield study reinforces that.
There is also a correlation between skeletal muscle and bone health – healthy muscles link to healthy bones, but strong bones do not necessarily mean that the muscles are strong.
Dr Low suggests: “It is important to perform early screening to identify those who have low muscle mass, so that appropriate interventions can be implemented.
“Muscle health can be determined by using a handheld dynamometer (to test hand grip), measuring calf circumference or measuring muscle mass using the bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA).”
The second phase 2 of the Shield study, to be completed this year, will involve 800 elderly participants at risk of being malnourished, who will be placed on oral nutritional supplements.
The aim is to find out how the supplement will affect their nutritional status, and their rates of hospital admission and re-admission.
The signs of muscle loss
Maintaining muscles during menopause
Carried out by researchers at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, the new study looked at 234 women aged 47 to 55, who were followed from perimenopause to early postmenopause, which is the stage after menopause when menstruation has permanently stopped.
The women had their muscle mass measured and hormone levels tested in the perimenopausal state and right after entering postmenopause.
The women were also asked to self-report their physical activity levels and wear an accelerometer for seven days, which is a wearable device that records movement.
The findings, published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, showed that the average duration of menopausal transition was one-and-ahalf years, although the researchers note that the time it takes to go through menopause is unique for each woman.
For some of the women in the study, it took less than six months, and for others, it took more than three years.
The researchers also found that during this time, the women experienced significant decreases in various measures of muscle mass, with an average of a 1% decrease in muscle mass.
However, women who were more active during the menopausal transition had higher muscle mass before and after menopause, compared to the less active women.
The researchers say this highlights the importance of keeping active during the transition from perimenopause to postmenopause, when the production of oestrogen stops and leads to a decline in muscle mass.
“We already knew that oestrogen has a role in the regulation of muscle properties,” says doctoral student Hanna-Kaarina Juppi.
“By following the hormonal status, measuring many aspects of muscles, and by taking into consideration the simultaneous chronological ageing of women going through menopausal transition, we were able to show that the decrease of muscle mass takes place already in early postmenopause.”
She adds: “The observed change does not seem like much, but what is meaningful is that the decline happens in a short period of time and can have an impact on metabolism, as muscles are important regulators of whole-body metabolism.” – AFP Relaxnews
Read more:
https://youtu.be/Umx6ywiJv_I
Others: One minute exercise cures: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/
⇒ Explore: COVID-19
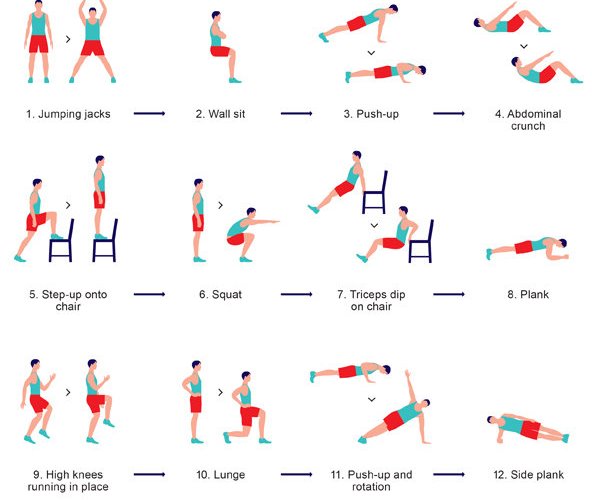
Protein shakes have divided nations! Some will be critical of the singlet toting gym junky’s protein shaker and others will feel inspired to shake themselves. So should you protein shake?
To shake or not to shake?
One quality scientific review, found protein supplementation with resistance training to increase muscle mass more than resistance training alone. Additionally, in conjunction with a healthy diet protein supplementation can aid in fat loss (1). A further review study found protein ingestion with resistance training to increase muscle mass, strength, explosive power and power during endurance based tasks more than resistance training alone (2). This tells us you should get shaking!
What, when, how to shake:
If it is an entire protein supplement you are consuming such as whey powder, then consuming the product within 30 minutes post workout appears to offer maximal strength and muscle mass benefits (3). Consuming protein after a workout becomes even more effective when it is consumed with a high GI carbohydrate like glucose or maltodextrin. Try adding a spoonful of honey to your shake or buy maltodextrin powder and add a sprinkle.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and one such amino acid is Leucine. It appears that protein supplements containing 3-4g per dose of leucine most optimise the amount of protein effectively used (synthesised) by the body. Consuming any normal whey protein should achieve this.
Alternatively, If you consume an isolated amino acid supplement (more expensive), you’re best taking this pre-workout. Although these are more expensive than protein supplements and confer no further benefit (3).
Is it healthful?
Fitness tips for menopause: Why fitness counts - Mayo Clinic
Taking Care Of Your Gut Is Key To Stronger Immunity | The Star
Covid-19 is turning out to be a disease with many faces as it can present with may different symptoms and signs.
http://mystar.newspaperdirect.com/epaper/viewer.aspx#
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT: 8 Exercises and Strategies to Treat it For Good
https://youtu.be/Umx6ywiJv_I
Others: One minute exercise cures: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/
Related posts:
When A Stroke Strikes
COVID-19's neurological symptoms; the next hotspots; COVID modelling
COVID-19 can affect the brain. How it happens and what to watch for.
⇒ Explore: COVID-19
Science on high intensity interval training: HIIT, or SHIIT?
HOW SCIENTIFIC IS THE SCIENTIFIC SEVEN MINUTE WORKOUT?

Weights and protein: Are protein supplements really the whey to go?
Protein shakes have divided nations! Some will be critical of the singlet toting gym junky’s protein shaker and others will feel inspired to shake themselves. So should you protein shake?
To shake or not to shake?
One quality scientific review, found protein supplementation with resistance training to increase muscle mass more than resistance training alone. Additionally, in conjunction with a healthy diet protein supplementation can aid in fat loss (1). A further review study found protein ingestion with resistance training to increase muscle mass, strength, explosive power and power during endurance based tasks more than resistance training alone (2). This tells us you should get shaking!
What, when, how to shake:
If it is an entire protein supplement you are consuming such as whey powder, then consuming the product within 30 minutes post workout appears to offer maximal strength and muscle mass benefits (3). Consuming protein after a workout becomes even more effective when it is consumed with a high GI carbohydrate like glucose or maltodextrin. Try adding a spoonful of honey to your shake or buy maltodextrin powder and add a sprinkle.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and one such amino acid is Leucine. It appears that protein supplements containing 3-4g per dose of leucine most optimise the amount of protein effectively used (synthesised) by the body. Consuming any normal whey protein should achieve this.
Alternatively, If you consume an isolated amino acid supplement (more expensive), you’re best taking this pre-workout. Although these are more expensive than protein supplements and confer no further benefit (3).
Is it healthful?