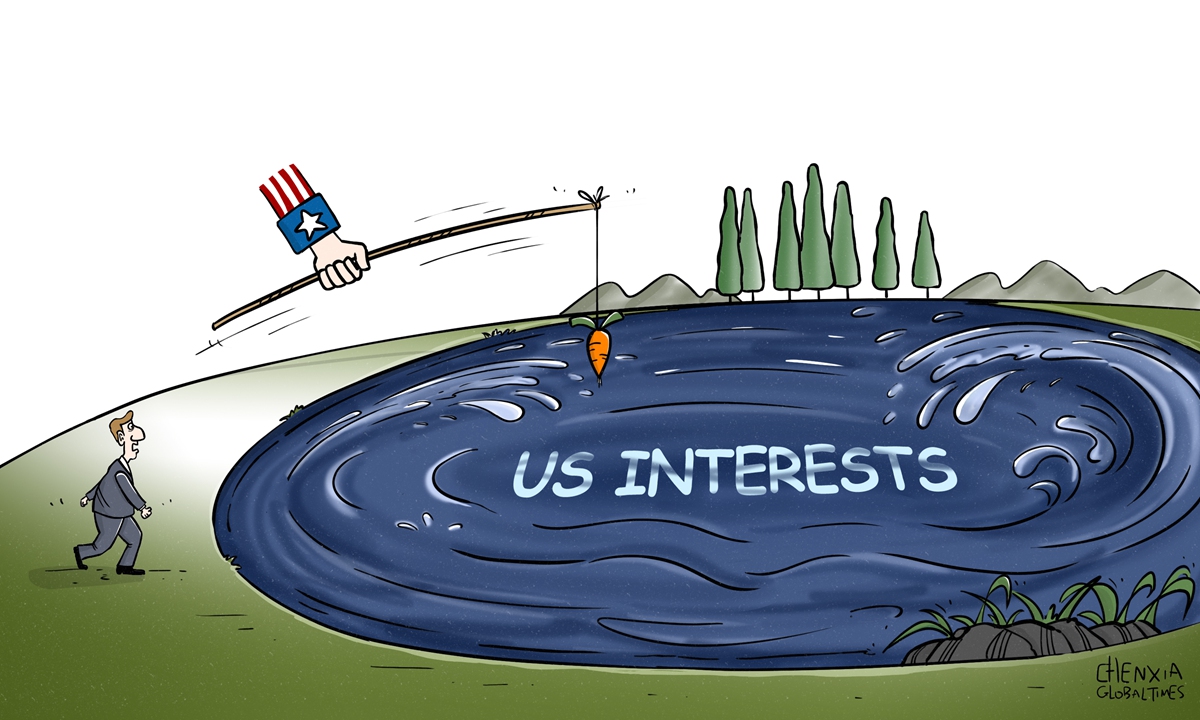
US 'Chips Alliance' scheme will exacerbate global chip crunch. Illustration: Chen Xia/GT
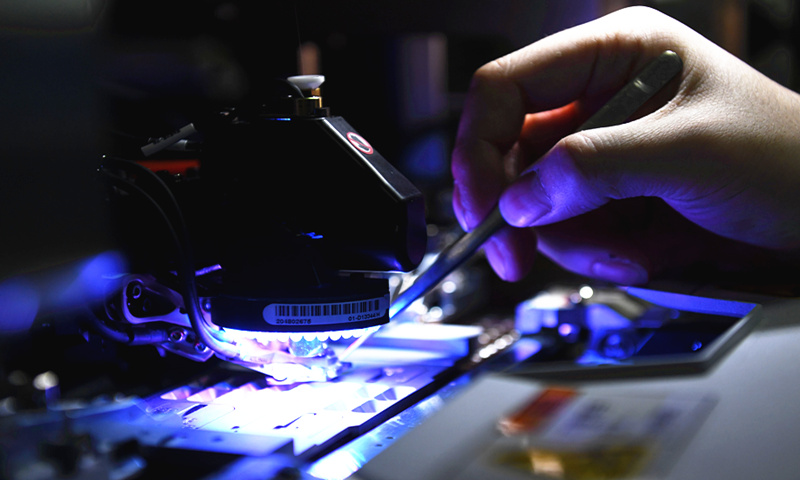
A chip manufacture machine Photo: VCG
The US Senate on Wednesday passed a chip bill that is intended to counter China's high-tech rise under the guise of shoring up US competitiveness and protecting national security, a "dream" that is very difficult to achieve considering problems like mounting debts and industrial hollowing-out in the world's largest economy, experts said. r countries and regions that have been kidnapped by the US bill to secede their chip supply chains from China, some might make symbolic gestures to follow the US orders but postpone real actions, like setting factories in the US, because what the US is pushing runs counter to their tangible benefits, observers noted. The bill, aimed at boosting US semiconductor production, passed the US Senate 64-33 on Wednesday and will move to the House and US President Joe Biden for approval, US media reported. The package, known as "CHIPS-plus," includes about $52 billion of funding for US companies making computer chips, a provision that offers a tax credit for investment in chip production, as well as funding to spur innovation and development of other US technologies, the report noted. Although US officials have used many expressions to justify the bill, like economic security, national security or "America's future," its real intention of containing China's development has nowhere to hide judging from the bill's requirement for companies to pick only one of two choices - business ties with China, or subsidies from the US government. The legislation would prohibit companies from expanding their semiconductor manufacturing in China for 10 years after they take a grant to build a US plant, Bloomberg reported on July 18. Companies could continue to invest in "legacy" chip manufacturing in China, but the definition of that term is unresolved. "The US is using the bill to force companies in countries and regions of key status on the global chip supply and industrial chains to play by US rules, as well as encircling and suppressing chip industries in emerging markets," Wang Peng, a research fellow at the Beijing Academy of Social Sciences, told the Global Times on Wednesday. Gao Lingyun, an expert at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS) in Beijing, told the Global Times on Wednesday that the bill is aimed at containing China's development and putting the US on a more competitive footing with China in the technological edge. Stuck in difficult position As US officials mount efforts to push the bill toward passage, which experts interpreted as shifting from a "stick" approach by forcing companies to leave China to a "carrot" tactic with subsidies as bait. Chip companies, either in the US or in other countries and regions, are finding themselves in the difficult position of having to take sides. A CNBC report noted that the CHIPS act has elicited divided responses from the US chip industry, as some players are concerned that the bill could provide disproportionate support to manufacturers like Intel while doing little to support other chip firms that do not produce chips by themselves. But even companies like Intel are not one hundred percent satisfied with the bill. According to a report from Politico, Intel and other chipmakers are lobbying to curtail limitations on their operations in China. Experts stressed that large US chip companies always know that globalized distribution is the best option for them, as the mode has supported their business growth over many years. "If companies build plants in the US, where do they get cheap labor and construction materials from? How do they cover their factory operating expenses? Why build a factory where the end market is far away?" questioned Ma Jihua, a veteran technology analyst. Xiang Ligang, director-general of the Beijing-based Information Consumption Alliance, said on Wednesday that for some large US companies, getting the subsidies and giving up the Chinese market will mean more losses than gains. For instance, Intel is unlikely to completely give up the Chinese market, which accounts for 20 to 30 percent of its entire annual revenue. For US allies like Japan and South Korea, whose semiconductor industrial chains are deeply integrated with the Chinese mainland market, the situation is even more difficult. "If they listen to the US, their companies might get tens of billions of dollars from the US, but they will lose hundreds of billions of dollars or even more due to decoupling with the mainland markets," Ma said. They will not only lose Chinese chip customers, but could also see spillover effects on other products as well, similar to how South Korean companies suffered in Chinese mainland market after the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) crisis, the expert said. Ma anticipates that Japan is prone to saying yes to Biden but would not cut its cooperation with China in reality, while South Korea is likely to face severe opposition from its large chipmakers. Xiang said that enterprises from Japan and South Korea may make some symbolic adjustments under this bill, like building factories in the US, but they may repeatedly postpone such investments because of the high cost of the technology. The US proposed the idea of the "Chip 4" semiconductor alliance and sent invitations to Japan, South Korea and China's Taiwan island. Though South Korea may ultimately join the bloc, Seoul's long hesitation to give a clear answer is evident of its dilemma. Plan invalid Experts said that the effect of the US chip bill may not meet the US' anticipation in reshaping the world's semiconductor supply chains, in which China now play an important role in producing parts. For example, Gao Lingyun from CASS said that the overall cost of making chips in the US is not very competitive on the global market, primarily due to its high labor cost, although it might have strong abilities in upstream industrial sections like research and development. "Past experience showed that efforts to set up a chip facility in the US, for example the US plant of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), has progressed slowly, which further underscores the difficulty of setting up chip factories in the US," he told the Global Times. Other factors are straining the US as well, such as mounting debts that are restricting Washington's abilities to materialize subsidies, their manufacturing hollowing-out that leads to insufficiency in everything from workers to materials, as well as the fact that the US might soon have another president, analysts said. According to Ma, there could be two results with the passage of the bill. First, it will not be implemented properly. Second, the US government could return to the "stick" approach if it receives scant support from companies. If the second way becomes reality, the world's semiconductor industry, which is already facing downward pressure, might enter a dark period with many companies going bankrupt, he said.
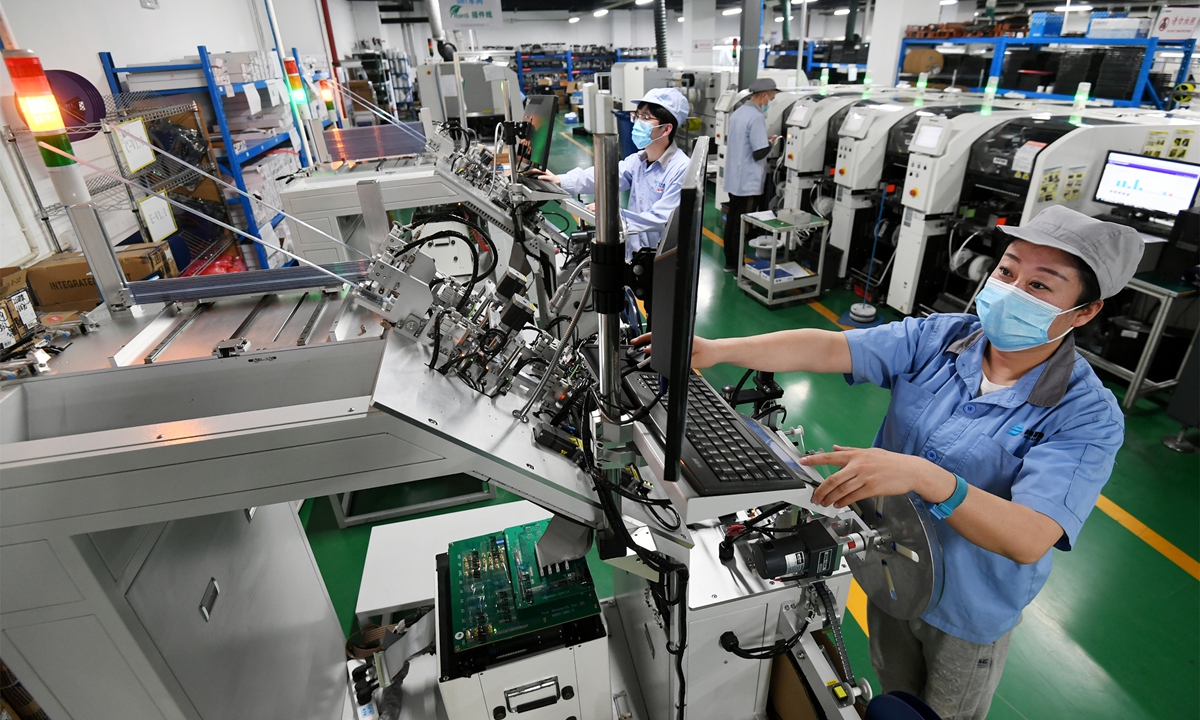 A worker checks a chip at Jade Bird Fire Co in Zhangjiakou, North China's Hebei Province, on March 27, 2022. Jade Bird makes firefighting products. Its self-developed Zhuhuan chip, which integrates fire detection capability, communication technology and integrated circuit technology, is widely used in China. Photo: VCG
China's rise
Despite US attempts to reshape the world's chip supply chains to a US-led one, China's chip industry is developing in a stable manner, be it the technologies or the markets, inspiring confidence among analysts that China will make breakthroughs in key chip technologies in about three to five years.
According to South Korean Customs statistics, South Korea's exports to China totaled $13.4 billion in May this year, while imports reached $14.9 billion, showing a deficit on the South Korean side for the first time, electronics information portal ijiwei.com reported.
One important stimulus for the situation is that China's exports of semiconductor products, which account for about one-sixth of the country's total exports to South Korea, surged 40.9 percent in the month, data provided by the Korea International Trade Association showed.
Besides, the rising popularity of China's electronic products like mobile phones has boosted demand for domestic chip products. For example, Chinese mobile phone brand Xiaomi recently launched a phone equipped with a China-made chip JR510, according to media reports.
On the technology side, Chinese companies are also making rapid progress. The country's chip giant Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp (SMIC) said it had made a breakthrough in the first generation FinFET technology and entered mass production in Q4 of 2019, while the tech's second generation, rendered equivalent to the 7nm and 5nm manufacturing process of TSMC, is also in a period of pilot production.
SMIC's profits surged 147.7 percent on a yearly basis in 2021 in yuan's terms, the company's annual report showed.
According to Ma, China's sense of urgency for chip industrial independence has enhanced a lot over recent years. This is giving rise to strengthened input, from the industrial, research and university sides, into the industry, bringing positive results such as a surge in chip product categories from hundreds to thousands.
In terms of technologies, China is also "leaping in progress," he said, adding that though China still has several technological bottlenecks to break through, it should be able to solve those bottlenecks after 3-5 years of stable development.
Xiang predicted that the large-scale storage in China's chip industry will start in 2023, as compared with chips from Europe, the US and South Korea, China's domestic chips are of good quality, priced about 60 percent lower than that of other countries.
A worker checks a chip at Jade Bird Fire Co in Zhangjiakou, North China's Hebei Province, on March 27, 2022. Jade Bird makes firefighting products. Its self-developed Zhuhuan chip, which integrates fire detection capability, communication technology and integrated circuit technology, is widely used in China. Photo: VCG
China's rise
Despite US attempts to reshape the world's chip supply chains to a US-led one, China's chip industry is developing in a stable manner, be it the technologies or the markets, inspiring confidence among analysts that China will make breakthroughs in key chip technologies in about three to five years.
According to South Korean Customs statistics, South Korea's exports to China totaled $13.4 billion in May this year, while imports reached $14.9 billion, showing a deficit on the South Korean side for the first time, electronics information portal ijiwei.com reported.
One important stimulus for the situation is that China's exports of semiconductor products, which account for about one-sixth of the country's total exports to South Korea, surged 40.9 percent in the month, data provided by the Korea International Trade Association showed.
Besides, the rising popularity of China's electronic products like mobile phones has boosted demand for domestic chip products. For example, Chinese mobile phone brand Xiaomi recently launched a phone equipped with a China-made chip JR510, according to media reports.
On the technology side, Chinese companies are also making rapid progress. The country's chip giant Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp (SMIC) said it had made a breakthrough in the first generation FinFET technology and entered mass production in Q4 of 2019, while the tech's second generation, rendered equivalent to the 7nm and 5nm manufacturing process of TSMC, is also in a period of pilot production.
SMIC's profits surged 147.7 percent on a yearly basis in 2021 in yuan's terms, the company's annual report showed.
According to Ma, China's sense of urgency for chip industrial independence has enhanced a lot over recent years. This is giving rise to strengthened input, from the industrial, research and university sides, into the industry, bringing positive results such as a surge in chip product categories from hundreds to thousands.
In terms of technologies, China is also "leaping in progress," he said, adding that though China still has several technological bottlenecks to break through, it should be able to solve those bottlenecks after 3-5 years of stable development.
Xiang predicted that the large-scale storage in China's chip industry will start in 2023, as compared with chips from Europe, the US and South Korea, China's domestic chips are of good quality, priced about 60 percent lower than that of other countries.
"In a sense, Chinese companies already have the ability to produce high-end chips, and they just need time to achieve mass production. The US chip blockade for China has in turn greatly facilitated the development of the country's chip industry," Xiang said.