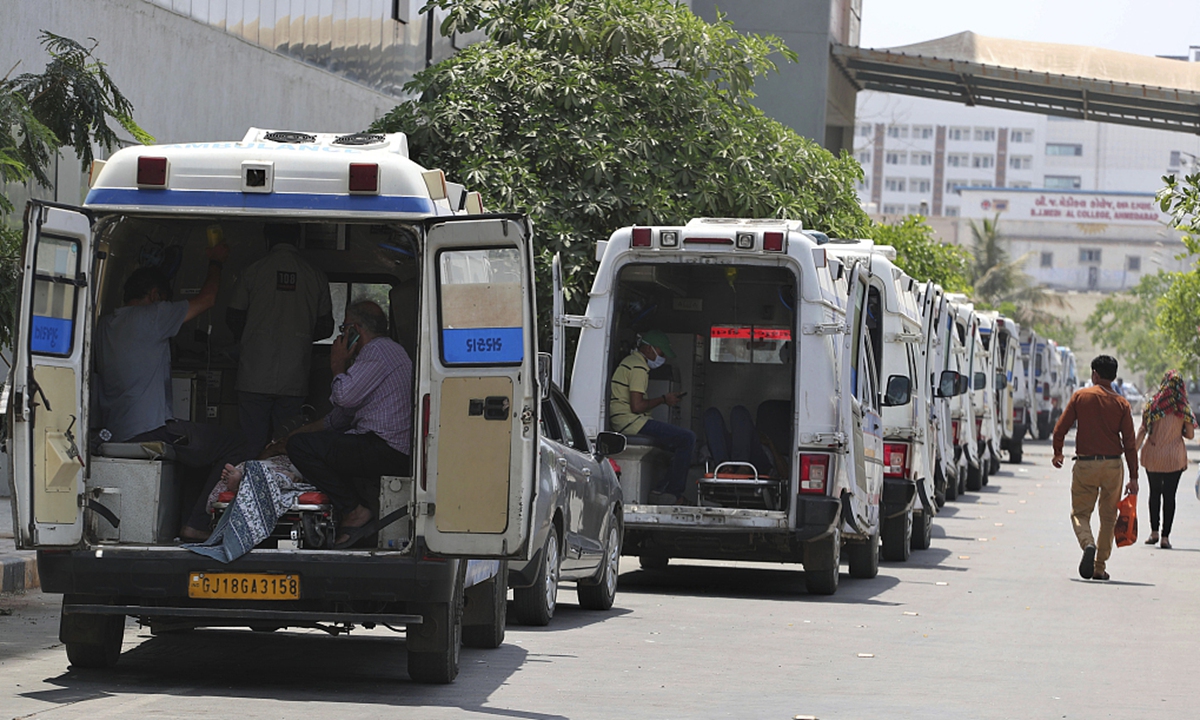
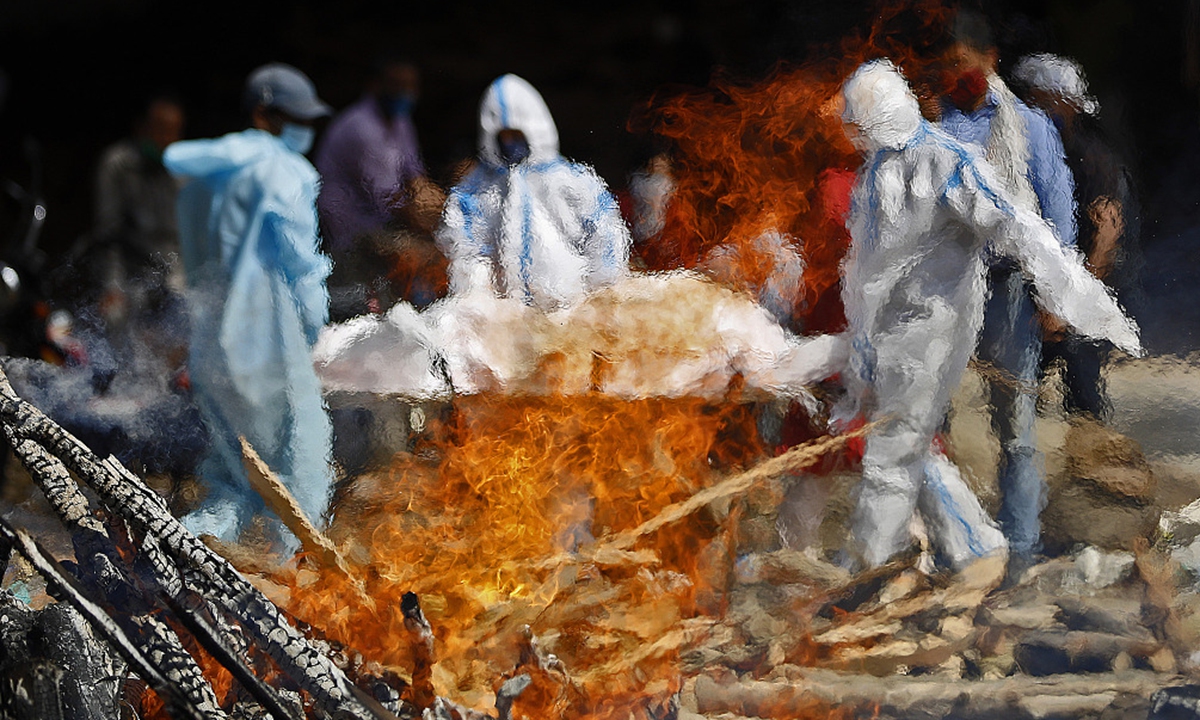
India is at a critical moment of fighting the virus. Yet some Indian media outlets and politicians are still manipulating politics, slandering China with an attempt to shift contradictions away from their failed policies. India has descended into a COVID-19 mess. Indian media and politicians should bear a large part of the blame. It's a tragedy for the Indian people.
In recent days, some news channels in India have been busy spreading the groundless conspiracy theories that "the coronavirus is a bio-weapon created in a Wuhan lab." As the new wave of COVID-19 wreaks havoc on India, they have hyped up conspiracy theories and old lies cooked up by some Western media and politicians last year, baselessly accusing China of "weaponizing the virus." Some Indian media's professionalism, cognition and sense of social responsibility are really jaw-dropping.
With India caught up in the crisis and as criticisms of the Indian government's response increase, the "lab leak" conspiracy theory has attracted some new attention in India, ranging from news channels to politicians. Earlier this month, some Indian ministers and BJP leaders shared an article on Twitter. The article warned Indians not to fall into the opposition's trap of making Prime Minister Narendra Modi the scapegoat. It said, "very few are talking about China and the possibility that the virus has been unleashed to weaken India."
The "lab leak" theory has been largely discarded by the world. A World Health Organization report in late March concluded that it's "extremely unlikely" that the virus was leaked from a lab. It's really ridiculous and clumsy for some Indian media outlets to flog a dead horse. And it's easy to figure out their real purpose.
Long Xingchun, a senior research fellow with the Academy of Regional and Global Governance at the Beijing Foreign Studies University and president of the Chengdu Institute of World Affairs, said the purpose of hyping the "lab leak" theory is obvious: deflecting public attention. With no sign of abating, the raging epidemic in India has aggravated public dissatisfaction.
By hyping-up the "lab leak" theory, some Indian media outlets and politicians are attempting to divert the public's anger to China. "For countries with an electoral system like India, the top consideration for some politicians is not people's health and lives, but votes. Accusing China of unleashing the virus to weaken India provides a good excuse for India to defend its anti-epidemic response and economic downturn," Long said.
China has refuted the lies of the "lab leak" theory many times. China has strictly fulfilled its obligations under the Biological Weapons Convention and does not develop, research or produce bio-weapons.
If the Indian media and politicians are really keen on figuring out whether the virus is a bio-weapon, they should ask Washington to clarify the US' biological militarization activities inside and outside the country and to disclose the real purpose of its more than 200 biological laboratories overseas. India could also demand an international inquiry.
It looks like some Indian media outlets and politicians are resorting to the old scheme of the former Trump administration, which tried every possible means to shift the blame onto China for its failed coronavirus response.
Just have a look at the results of Trump and his failed secretary of state Mike Pompeo. They didn't focus on fighting the epidemic, but instead played tricks to politicize the virus, concocting political manipulations to discredit China. As a result, the US witnessed the highest COVID-19 death toll. This became the main reason why Trump lost the election.
Since the second wave of COVID-19 outbreak hit India, China has expressed its goodwill and taken concrete actions to provide necessary support and help to India. China has sent life-saving supplies such as ventilators, oxygen generators, masks and medicines to India. This has shown China's goodwill and humanitarianism.
However, some Indian media outlets and politicians are requiting kindness with ingratitude. They have slandered China's help, tried to play the Taiwan card, attempted to sow discord between China and neighboring countries, and devilishly spread rumors and lies to discredit China. They are shameless and have no moral bottom. What they are now doing is no different from creating a humanitarian disaster in India. It's the Indian people that will have to bear this egregious suffering.
Share This
Saturday, May 22, 2021
Lame Indian media and politicians resort to ‘lab leak’ lie to shift focus
 Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Monday, May 3, 2021
The virus is back! Bond formed through China’s support for India’s anti-epidemic fight overrides irrational public sentiments toward another
The virus is back, this time with more energy, tactics and camouflage.
We don't cough
No fever, it's joint pain, weakness,
Loss of appetite and Covid pneumonia!
Of course, the death rate is higher, it takes less time to get to the extreme. Sometimes no symptoms ... let's be careful ...
The strain is not domiciled in our nasopharyngeal region!
It directly affects the lungs, which means window periods are shortened.
I have seen a number of patients without fever, but an x-ray report shows moderate chest pneumonia!
The nasal swab is often negative for COVID19!
There are more and more false pharyngeal nasal tests COVID19) ... which means that the virus spreads directly to the lungs causing acute respiratory distress due to viral pneumonia! This explains why it has become acute and more fatal !!!Covid21
Be careful, avoid crowded places, wear a face mask, wash our hands often.
*WAVE* more deadly than the first. So we have to be very careful and *take every precaution.*
Indian mutated virus reached Malaysia!
Malaysia reports first case of Indian COVID-19 variant ...
中国制氧机到了!印度网友啥反应?看清了美国的虚伪面目吗?
印度疫情“令人窒息” “美国优先”火上浇油
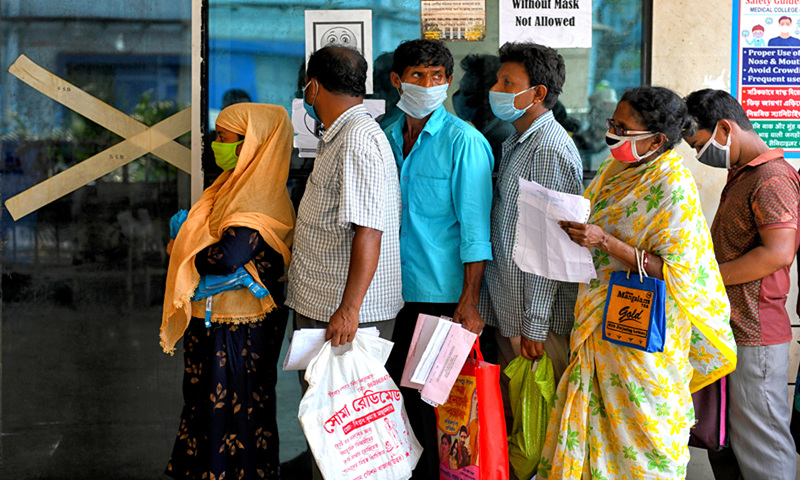

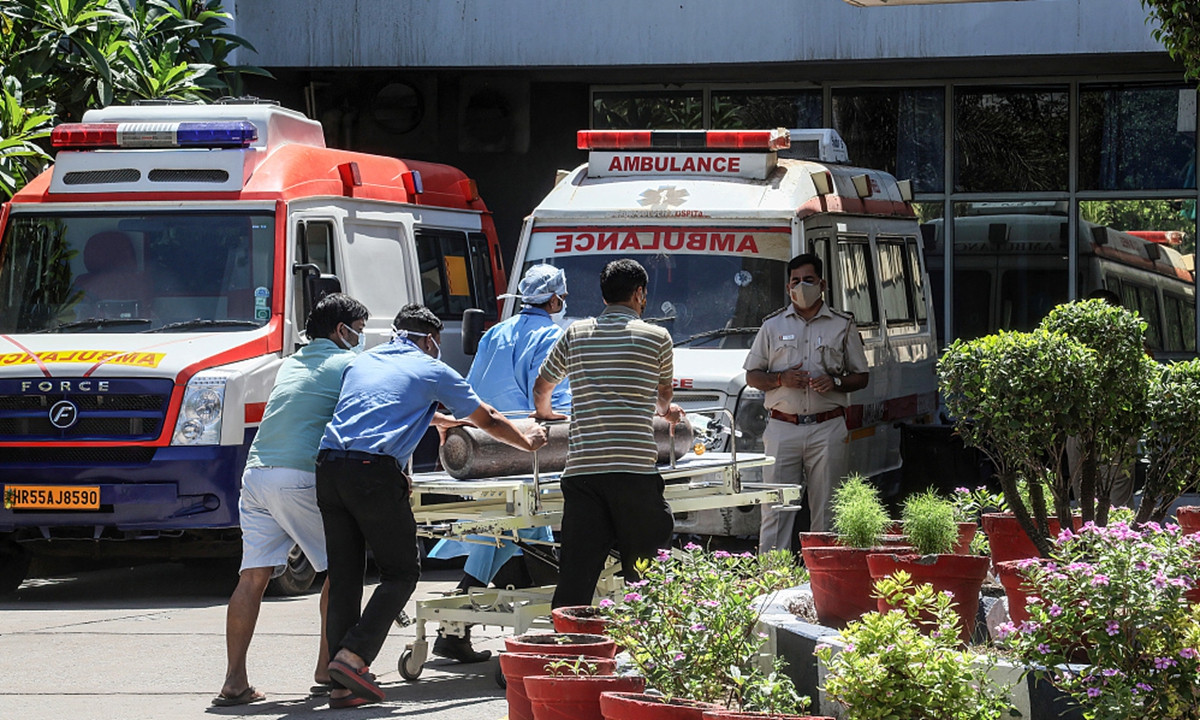
Indian people with COVID-19 symptoms queue for an Antigen Test at a government hospital. Photo: VCG
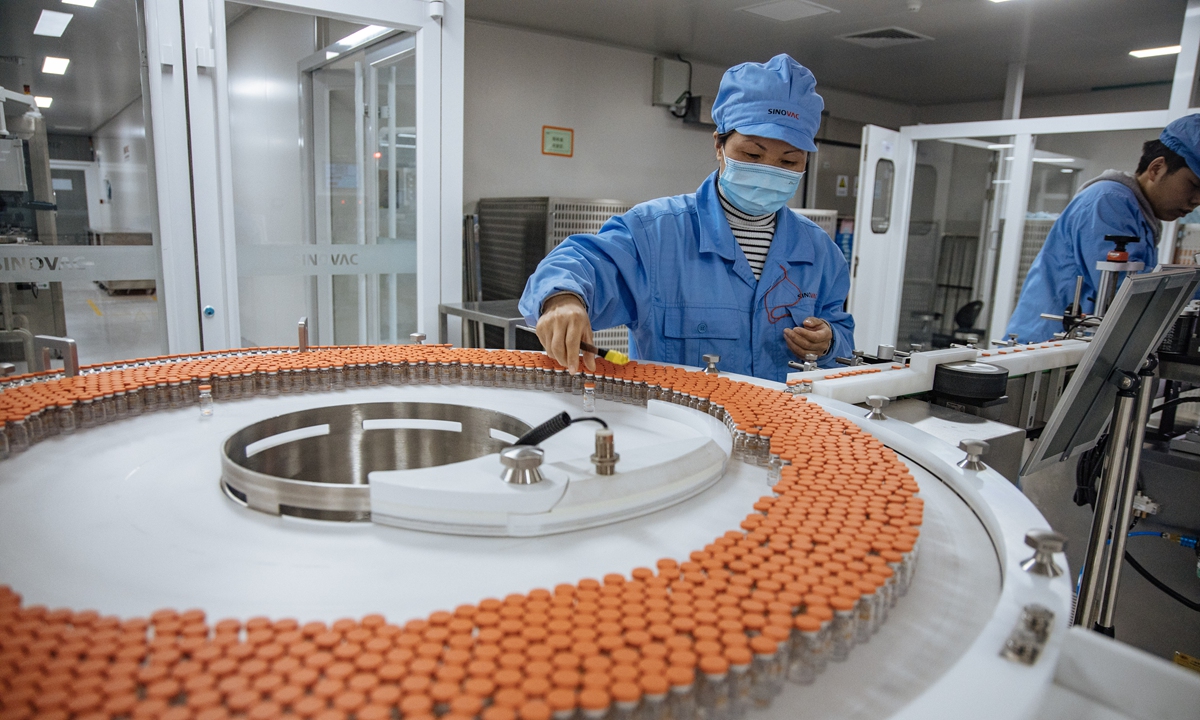
India’s COVID-19 epidemic has continued to rage on. China has become India’s largest supplier of crucial anti-epidemic supplies such as oxygen generators and ventilators. So far, China has provided India with more than 20,000 oxygen generators and 5,000 ventilators. India has submitted orders to Chinese companies to produce over 40,000 units of oxygen generators. However, Indian public opinion has not expressed its gratitude toward China for the emergency supplies, or it can be said that grateful voices have been very few. In contrast, many narratives have stressed that China's supplies are not aid, accusing China of “exploiting the opportunity to make money,” and claiming that it has "geopolitical intentions" to export these goods to India. Such rhetoric in India is in sharp contrast to their high-profile publicity on help from the US and the West. The Chinese people will certainly be disappointed after reading such opinions.
In terms of public opinion, Chinese and Indian societies have not got along well. Border tensions last year escalated sentiments on both sides, leading to a confrontation of public opinion. India has leaned closer to the US, further solidifying the social divide between China and India. This has become the background in which India is dealing with China in the face of a crisis.
China has made the greatest contribution to India’s current fight against the epidemic. Instead of being purely symbolic, China’s support and help has been very substantial. There is no atmosphere of public appreciation of China’s help in India. There is still a lot of resentment over border frictions and strategic hostility toward China. Out of a sense of pride, India has taken a lot of goods from Chinese companies, but has remained silent toward the fact. Hindustan Times has listed ten countries and regions that have started sending relief materials to India, and what kinds of materials they have supplied. But China is not on the list.
In the face of such a response from India, what should we do? Should we publicly accuse India of “repaying good with evil?” or turn our long-standing grievances toward India into mockery, even gloat about the Indian epidemic? I don’t think it is appropriate for us to be overly sensitive toward India’s reaction, especially going further to mock India's failure to fight the virus.
The official mindset of Chinese society toward India’s epidemic situation must be sympathetic and supportive of their battle against it, and this is indeed the case. I don’t think it’s proper for social media accounts of certain Chinese official institutions or other influential forces to mock India at present.
India has indeed done something wrong toward China. Even today when India is in trouble and China is lending it a helping hand, India still holds a grudge and remains narrow-minded. But currently, our prevailing attitude toward India should be still to show our sympathy and support, without being distracted by other sentiments. There is plenty of time and occasions for us to express our views regarding India. And we do not have to speak up upon them when India is struggling against the virus. We should not respond to radical voices in India, instead we should avoid escalating the spat between China and India among public opinion.
Although India has talked little about it, we have to say that China has done a magnificent job in supplying and supporting India. It is necessary for us to make the world more clearly aware of China’s actual role. Meanwhile, not like the US, the Indian government has not attacked China’s fight against the virus, nor has passed the buck to China. Currently, India is not only falling into a humanitarian disaster, but has become weak in the eyes of the rest of the world. The Chinese government proposed to offer India necessary support and assistance much earlier than Western countries. And our supplies have been provided to them with amazing speed, faster than any other country.
I understand that there are many voices and the public has their right to express various sentiments toward India. So do some figures who have many followers on social media platforms. But our public opinion, especially mainstream opinion, needs to follow the Chinese government’s narratives and moves as a whole, forming the tone of sympathy and support for India's fight against the virus. This is an indispensable part of China's national image.
We need to believe that actions speak louder than words. China’s supplies play a crucial role in India’s battle against the virus. We cannot ignore border frictions between China and India, but the bond formed through China’s substantial support to India’s anti-epidemic fight is also there. China and India are neighbors that cannot be moved away from each other. Apart from many frictions, China is India’s close neighbor which is better than a distant relative in the critical time of a crisis. As long as China does its best to bolster India’s fight against the virus, it will certainly become a factor in shaping Indians’ general perceptions of China.
China is a big country with a long history of civilization. Our national and international outlook has been shaped through thousands of years of experience. We should not be influenced by the logic of power which has been prevailing in the US and the West. When stepping up the construction of hard power, we cannot neglect the significance of “convincing people by virtue.” For China, virtue is not hypocrisy. Instead, it is our dignity and strength, which is one of the cornerstones of our international mobilization.
Chinese Ambassador to India’s quick response to India’s Bollywood Actor Sonu Sood’s tweet which alleged that China has ...
The White House on Friday announced travel restrictions on India effective on May 4 due to high COVID-19 ...
In helping India fighting COVID19, China will: support firms accelerating production of medical supplies; facilitate customs & transport ...
Related posts:
A patient suffering from the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) receives treatment inside the emergency ward at Holy Family hospital in New Delh.
 Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Monday, April 26, 2021
The world hijacked by Washington’s selfishness, Should India thank US' belated aid? 第三波疫情猛如虎 !
Video https://www.globaltimes.cn/video/#.YIbAJJ1_i1s.twitter
Bagaimana Tsunami Covid Di India Boleh Berlaku
China and India should put their differences aside and join forces in fighting pandemic
More than a quarter of Americans are fully vaccinated against the coronavirus now, while about 40 percent of people in the US have received at least one shot. Not everyone wants to get vaccinated, so it is predicted that there will be a surplus of vaccines in the country after mid-May. At the same time, many developing countries are suffering vaccine shortage. In Namibia, an African country with a population of 2.5 million, only 128 people have received two doses of a vaccine until now.
The ugly "America First" doctrine on vaccines was fully revealed by the coronavirus outbreak in India. A humanitarian disaster has developed in the country. However, India's call for Washington to ease curbs on the export of vaccine raw materials was rejected. US State Department spokesperson Ned Price said Tuesday that the priority of the country is "ensuring the distribution of a safe and effective vaccine to millions of Americans, to all Americans who are able to take advantage of it." Washington also turned down calls from India, South Africa and others to waive patents on COVID-19 vaccines.
To date, the US has made almost no actual contribution to the global fight against the pandemic. As the most developed country in the world, it did a poor job in the epidemic fight, failing to contribute any positive experiences to other countries. The country imported a huge amount of supplies such as masks and ventilators that were in short supply in the world last year. Washington undermined global cooperation against the virus by attacking the World Health Organization for quite a long time. The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is Washington's most important product to fight against the pandemic. But until now it has been used primarily to protect Americans and a limited number of US allies.
"America First" is a very crude principle. It has become a practical guide to bipartisan actions in the US. The former administration of Donald Trump had both said and acted according to this principle. Although the Biden administration hasn't talked about it, it is in fact also acting in line with the principle.
Transmitted to the political center through each American constituency, the US' selfishness has formed a kind of "rightfulness" under American democracy. Meanwhile, Washington is keen to promote its idea of "human rights" to the world. It acts like it has compassion for all humanity, and surprisingly, it does not feel awkward about it at all.
The world cannot allow the US to abuse the right to define international justice. Washington has refused to share vaccines with developing countries proportionally. The world should jointly condemn it, making Washington bend its head, like a rat scurrying across the street with everybody chasing it. However, till today, the US is still arrogantly claiming it is a global moral leader. It even accuses China and Russia's efforts to share vaccines of being "vaccine diplomacy." The US has totally called white black and black white.
The US has misled and hijacked various countries' national security concept. This is where its arrogance comes from. The world is in an era of peaceful development, but US elites have successfully fanned many countries' anxieties over geosecurity, as the US is the one who has the most abundant resources to play the geopolitical game. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is the biggest security shock that countries have encountered in recent years, but many countries have deeply fallen into the geopolitical myth and been hijacked by Washington. Therefore, they indulged Washington's misdeeds.
India in fact has become a victim of the US tricks. India already had an economic slump before the outbreak of the pandemic. India's relations with China have been manipulated by the US so severely that even its vaccine assistance provided to other countries took China as a target. However, now India has suddenly become the epicenter of the global pandemic. It is caught in a predicament where it is unable to deal with the situation by itself, receives no support from the US, while it is too embarrassed to accept China's help.
In short, the US has caused harm to the whole world in recent years. Despite being a self-proclaimed world leader, it failed to act as a responsible power in terms of economy, security and the anti-pandemic fight. However, Washington has managed to keep the "moral high ground" and issue orders. It is fair to say that it is the world, including countries like India, that has indulged it. We are suffering a tragedy caused by ourselves.
Should India thank US' belated aid?
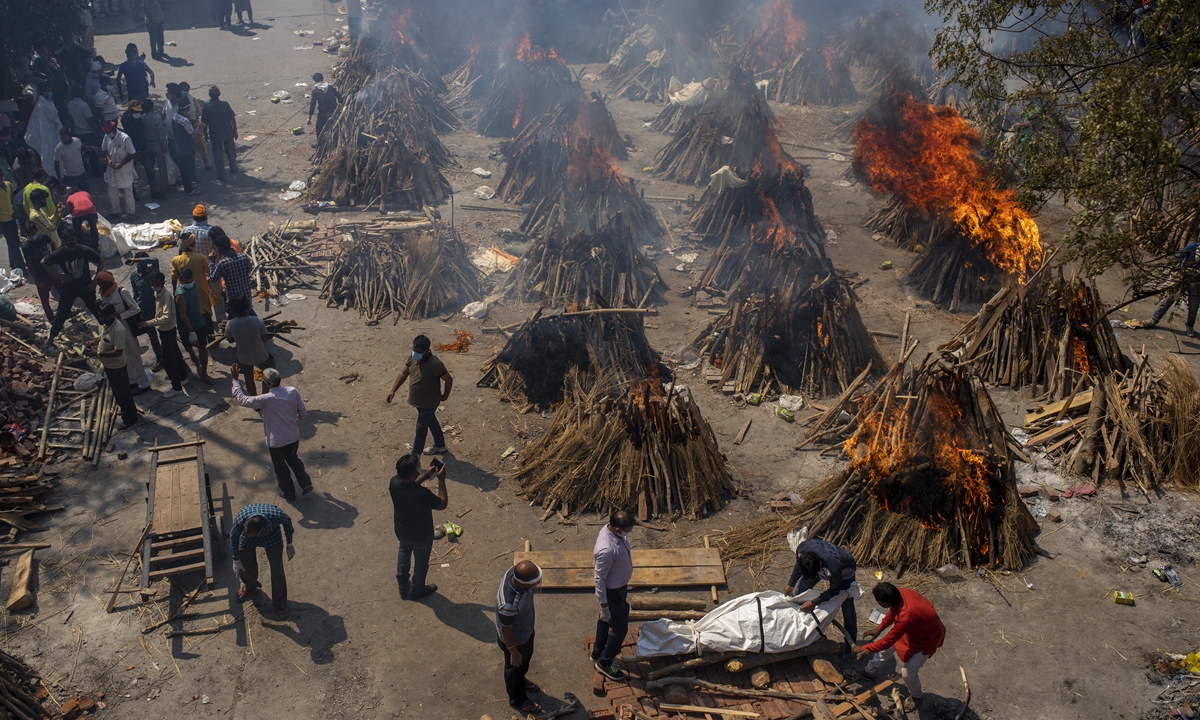

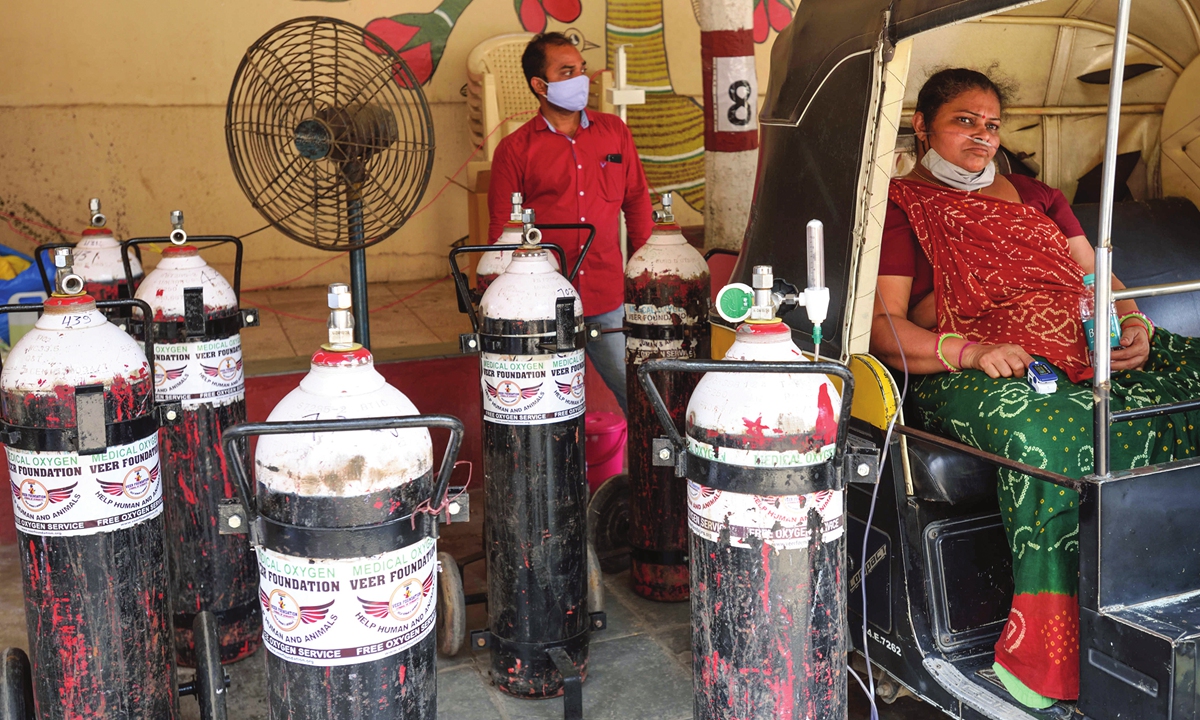
Multiple funeral pyres of COVID-19 victims burn at a site converted for mass cremations in New Delhi, India on Saturday. Indian authorities are scrambling to get medical oxygen to hospitals when the country reported a new global daily record of more than 346,000 infections for a third straight day. Photo: AP
Under great pressure from international public opinion, US President Joe Biden said on Monday the US is determined to "help" India. It's reported that more than 300 oxygen concentrators have been dispatched from New York on Sunday morning and are supposed to arrive in New Delhi on Monday. This was in sharp contrast with the US' negative attitude toward assisting India until last week.US allies including the UK, France, and Germany also announced to offer assistance to India on Sunday, which left people with an impression that Washington has coordinated with them.
Many Indians are complaining that the US aid comes way too late and is more of symbolic significance. Several hundred oxygen concentrators are inadequate for India. What the country needs now are tens of thousands, or even hundreds of thousands. The US will immediately deploy supplies and other assistance, including raw materials for COVID-19 vaccine, to India, the White House said, following a Sunday call between US National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan and his Indian counterpart Ajit Doval. But the US will still have reservations over the quantity of material exports, and the implementation process will face challenges.
Biden's approval rating stands at only 52 percent after almost 100 days in office, the third-lowest since tracking began in 1945, following Donald Trump and Gerald Ford. Biden is facing enormous pressure from the Republicans and some Democrats. "America First" has been deeply embedded into the values of the US and has become a red line that Biden dares not touch.
There are two reasons for the US' strategic selfishness. First, this is the inherent nature of the US system, which is prone to amplify individual selfishness rather than restrain and counterbalance such selfishness. Second, the US has become relatively weak, and it cannot meet its "leadership role." India is a country with an enormous population. In the long run, it will cost US much more to "lead" India than any of its other allies.
One unhealthy aspect of the global anti-pandemic fight is that science and humanitarian logic have failed to truly dominate the fight on the international stage. Geopolitical thinking has never been away from the fight. It has disrupted the pandemic fight from time to time, and even managed to play a dominating role at some moments. India has been struggling in a critical situation, but geopolitical clues are still evident in its epidemic-related information. This is regrettable. COVID-19 patients are dying in batches, but some people are still debating which country's assistance India should take and what it would mean for international relations in future.
Whatever happens, we hope India could curb its epidemic as soon as possible. Mankind is a community with a shared future when it comes to the fight against the pandemic. As India is a large country¸ the raging epidemic in India inevitably means increasing risks for other countries and regions. How India can realize a soft landing with a lower death toll will offer useful experience for other developing countries.
The new coronavirus variant detected in India seems to be able to ferociously spread with the approach of summer, which requires higher international vigilance. India's tsunami-like COVID-19 wave warns us that fighting the coronavirus pandemic is a long-term "world war" and many unexpected new battlefields and new battles may await us. We can never let our guard down.
Countries with a strong capability to resist COVID-19 have to assume greater responsibility. It is vital that the US joins them. The US has made little positive contribution to the global fight against the pandemic. Lending a helping hand to India can be seen as the first US attempt to play such a role. We hope it will be Washington's turning point. The US has gravely dragged the global fight against the pandemic, and it is supposed to proactively make up for it.
Since last year, the novel coronavirus pandemic has hit many countries and regions in the world, resulting in unbelievable deaths and economic losses. But some countries are still building their national security in traditional ways. This is a strategic mistake, at least to some extent. Washington has played a misleading role in this regard. In other words, if the US is drunk, many other countries may not be able to remain sober.
第三波疫情猛如虎
“加拿大”禁止航班的进出,每天死亡人数超过1000人。
“沙特阿拉伯”封锁,没有进出航班。 “坦桑尼亚”紧跟国际形势全面封锁。
“巴西”跌入了最致命的篇章,今天有4100多人死亡。
“西班牙”也已宣布可延长紧急状态。
“英国”宣布为期一个月的封锁。 “法国”2周封锁。 “德国”4周封锁。 “意大利”今天也紧跟随其后。
“所有”这些国家/地区已经确认“第三波COVID19 ”比第一波致命。 因此,我们必须非常小心,并采取所有预防措施。
成为朋友和家人之间的警报沟通者。“从第三波中拯救每个人”。 “不要以第二波封锁阶段”没发生什么来作判断 ...
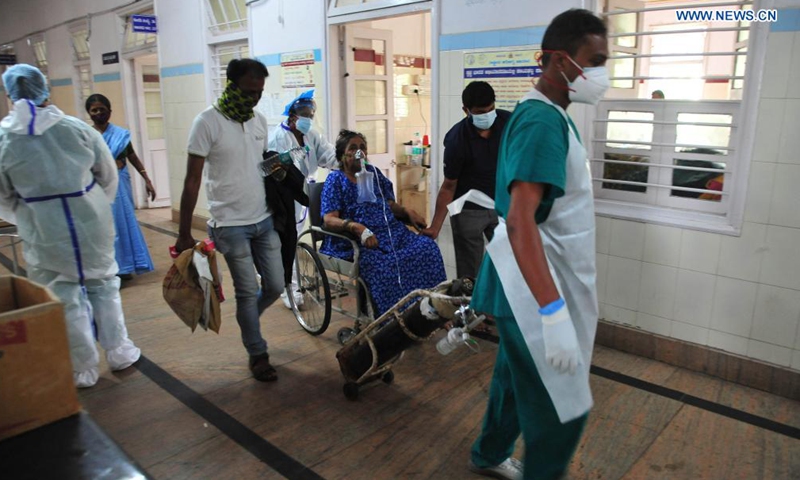
近期更可怕疫情发生在拥有I3亿人口的印度。因防疫松懈,病毒双重突变,致疫情全面失控。4月4日首次突破10万例,4月I5日单日新增破纪录20万例,22日首超30万例,24日首超33万例。而且全国缺乏氧气,缺乏口罩及抗疫资源,并正成为新的双重变异病毒的总爆发点,并向多个国家漫延。
“历史告诉我们,与1917年至1919年的西班牙流感一样,第三波比第一,二波更危险。 数百万人死亡。
” “保护好你自己和你的家人”。 保持生物安全措施,戴口罩,保持社交距离,勤洗手等。
历史不会说谎,让我们反思。
__________ _______
不要自己保留此信息,要与家人和朋友分享。 提高警惕!
 US needs to be more sincere in its vaccine exports: Global Times editorial
US needs to be more sincere in its vaccine exports: Global Times editorial
There are doubts that Washington is not sincere enough about providing COVID-19 vaccines to other countries. The world would wonder why it is AstraZeneca but not Pfizer?
America, it's time to cleanse your own stains
The US is a country that boasts of its so-called deep-rooted ideal of democracy, rights, liberty, opportunity and equality. But how can a self-portrayed perfect country become one of chaos, division and inequality as we see today? Is it because ...
The US government needs to reflect on and adjust its policies. The “America first” policy has to give ...
US sits on stockpile as others beg
When the US sets priority on vaccines, it takes it, even as many countries in the rest of the world ...
With India suffering from the virus, Pakistan has put aside past enmity to provide aid. India should reflect ...
Americans are particularly adept at expressing emotions. It is bizarre how belated and reluctant aid actions can be ...
Experts warn of new Covid strains | The Star
.
 Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Sunday, March 21, 2021
Bitcoins, Cryptocurrencies under fire
India and China come down hard due to concerns of financial market stability, illegal fundraising
N THE latest twist involving the world of cryptocurrencies, India’s government plans to impose a massive ban on the asset class.
Reports have indicated that the Indian government plans to pass a bill that would ban just about every activity involving cryptocurrencies, including the possession, issuance, mining, trading and the transferring of crypto-assets.
Once passed, this would make it one of the world’s strictest policies on cryptocurrencies. Government officials have said that the move is because they believe cryptocurrencies threaten the stability of financial markets, tend to fund unlawful activities and even resemble ponzi schemes.
The move by the Indian government falls in line with the school of thought that cryptocurrencies could increasingly suffer bans by governments around the world.
In India’s case, the move comes after an earlier ban two years ago. But last year, the courts in India overturned the decision, citing the ban as “disproportionate” after cryptocurrency exchanges filed a lawsuit against the central bank’s ban.
The strong stance against cryptocurrencies has also been shown by China’s government. More than three years ago, China was the first country to ban initial coin offerings (ICOs), calling it “illegal fundraising”.
Since then, the Chinese government has accelerated efforts to clamp down all businesses involved in cryptocurrency operations, including bitcoin miners.
China’s government says its stance is based on investor protection, money laundering concerns and the unnecessary consumption of energy due to crypto mining activities.
Last month alone, there were plans to ban new cryptocurrency mining projects and shut down existing ones in China’s Inner Mongolia region.
As one financial analyst puts it, “the problem with cryptocurrencies is that while it thrives to work in an unregulated world, it is bound to come under the scrutiny and regulation of governments, which are mostly afraid of its misuse and potential negative impact to financial markets. Perhaps somewhere in the future, a balance will be struck but that is anyone’s guess”.
While governments have a tendency to ban cryptocurrencies, many are embracing blockchain technology with the intention of issuing state-backed digital currencies.
This is essentially an electronic version of notes or coins which would replace physical cash entirely and dubbed central bank digital currencies or CBDC.
China is one of the leading countries for this and has already passed a law to legalise its own official digital currency. Similarly, India is an example of another country that is considering having its own digital currency. Interestingly, India’s move to pass the bill to ban cryptocurrencies comes soon after the mother of all cryptos, namely, bitcoin has hit its all-time high past US$60,000 (RM246,449) for the first time earlier this week.
The world’s biggest currency rally was driven by speculative demand, increased adoption by firms and institutional investors that see bitcoin as a store of value. Last month, Tesla bought over a billion dollars worth of bitcoins.
The electric car maker said it plans to accept the digital coin as payment for its products. Mastercard has also said it would also soon accept bitcoin as a form of payment.
Asset manager BlackRock and payment companies Paypal and Square have also recently backed cryptocurrencies.
Back home, the question remains whether the government, central bank or the Securities Commission (SC) would take a stronger stance against cryptocurrencies.
Malaysia’s regulators have held the view that digital assets are not legal tender and have warned investors to be cautious when dealing with cryptocurrencies.
SC chairman Datuk Syed Zaid Albar tells StarBizWeek that “investors must understand that unregulated, offshore investments are not protected under Malaysian securities law”.
“The SC has put in place a regulatory framework for such new emerging investment channels to provide certainty to issuers and investors who are keen to explore these new instruments.
“For example, our regulatory framework has tried to address issues such as putting investors’ money in trust accounts, accurate disclosures, cooling-off periods and conflict of interest situations are also regulated, ” Syed Zaid explains.
The country’s central bank, Bank Negara, also echoes a similar view, explaining that digital assets lack the characteristics of money and suffer from several limitations such as price volatility and risks of cyber threats.
“Digital asset activities are also subject to anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regulations administered by the respective authorities, ” the central bank reported in its annual report in 2019.
Malaysia is also one of the countries studying the feasibility of issuing its own digital currency. “The bank is no exception, and we continue to engage closely in discussions surrounding CBDC with other central banks, ” it said.
More collaborations among central banks around the world are taking place to study the impact of a digital currency for financial stability and the monetary policy of a country.
Why does Bitcoin use 10 times more electricity than google...

Google’s entire operation consumed 12.2 TWh in 2019 and all the datacentres in the world, excluding those that mine Bitcoin, jointly consume around 200 TWh annually. — Reuters
Related posts:
Blockchain: Internet of Value/ Currency of Trust; Private cryptocurrency a misallocation among blockchain technology, say research & economist
China gets into blockchain race with US
China's new digital currency
On Mcoin, Bitcoin and points of investment
Bitcoin: Utter pipedream
Blockchain Festival & Conference Week, Kuala Lumpur 26~27 Sept 2018

SC to regulate digital assets
Bitcoin, digital currencies rally, caution prevails; virtual currency in property
Jack Ma Embraces Blockchain for Ant But Warns of Bitcoin Bubble
What is Blockchain Technology, its uses and applications?
JPMorgan CEO warns he will fire any employee trading Bitcoin for being “stupid.”
Environmental impact of cryptocurrency
Bitcoin falls after exchange is hacked, US$72 mil stolen from Bitfinex exchange in HK
 Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Sunday, October 6, 2019
China in the Asian century, Is the future truly Asian?
 |
| Rising together: No, Chinese imperialism is not simply replacing US imperialism, as China emphasises win-win partnerships, says Prof Zhang. — Handout |
China in the Asian century
PROF Zhang Weiwei is among the most respected scholars in China today. He is a leading expert on China’s “reform and opening up” policies and its status as a “civilisational state.”
As director of the China Institute at Shanghai’s elite Fudan University, he is also professor of International Relations and had served as English interpreter for China’s Paramount Leader Deng Xiaoping. In an exclusive interview earlier in the week, Prof Zhang spoke to Sunday Star about future prospects with China.
As the leading authority on China’s civilisational state, how would you define it, as distinct from a nation state?
With China, it’s a combination of the world’s longest continuous civilisation and a super-large modern state. A civilisational state is made up of hundreds of states amalgamated into one large state.
China is a modern state respecting international law like a nation state, but culturally diverse, with sovereignty and territorial integrity.
There are four features of China’s civilisational state: a super-large population of 1.4 billion people, a continent-size territory, significant culture, and a long history.
If we are returning to an East Asian tributary system, what changes can we expect in China’s policies in this region today?
The tributary system is a Western name for China’s relations in this region (in the past). China is a “civilisational” – as an adjective – state, a modern amalgamation of many (component communities).
During the Ming Dynasty, China was a world power – but as a civilizational state more than a nation state – and did not seek to colonize other countries, unlike Western powers that were nation states. Since then, China’s status and capacity as a nation state has grown significantly. Will it then become more like Western powers now?
China today is a nation state, but different from European (nation) states. It is also still a civilisational state.
The Chinese people are not just Han, although the Han majority is 92%. There are 56 ethnic groups in China, (mostly) minorities.
But China rejected the Permanent Court of Arbitration’s ruling on the South China Sea, initiated by the Philippines, which found China’s claims insupportable.
The tribunal was illegal; it had no right to make such decisions. The Permanent Court of Arbitration is not part of the United Nations.
How can countries in South-East Asia be convinced that the rise of China will not simply result in Chinese imperialism replacing US imperialism?
China emphasises win-win partnerships, such as in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). It encourages discovering, building, and benefiting together.
Countries in South-East Asia join the BRI out of their own interest. It is not something imposed by China.
Some countries have described the Second Belt and Road Summit this year as being more consultative than the first. As for the future?
The future Belt and Road Summits will be even more open and consultative.
Is the current US-China trade dispute only a symptom of much larger differences, such as a historic divide in the reshaping of a new global order?
It is more than about trade. With the United States especially, it is zero-sum, but for China it is win-win.
The Chinese economy is larger than the US economy, or soon will be. (In PPP or purchasing power parity terms, China’s economy grew larger than the US economy in 2014.)
The United States is trying to decouple its economy from China’s. How can China ensure that it would not only withstand these efforts but also triumph?
The attempt to decouple the two economies will fail. About 85% of US companies that are already in China want to stay.
Looking at the trade structure, most Chinese exports to the US are irreplaceable. No other place in the world gives a better price-quality ratio in manufactured goods.
So the US cannot win in this decoupling because there are no alternatives (as desirable producing countries). China has the world’s largest chain or network, or factory clusters, for all kinds of goods.
How likely do you see a hot war – more than a trade war or a cold war – breaking out between a rising China and what is perceived to be a declining United States?
The US knows that it won’t win (a hot war). No two nuclear-armed countries will go to war. It would be very messy.
So far no two nuclear-armed countries have fought. There may be a small likelihood of direct confrontation, but not a war situation.
No commercial shipping has been interrupted by China. So the US need not worry.
Can Asean, or an Asean country like Malaysia, help to bring the United States and China closer together as partners rather than as rivals?
Possibly. Malaysia perhaps can help, as it is friendly to both China and the US.
As China continues in its rise, what steps is it taking to provide for more cooperative and consultative relations in this region?
Trade between China and Asean countries, for example, has grown, and has now exceeded China-US trade.
Generally, China’s relations with Asean countries are quite promising, with Free Trade Area relationships as well.
By Bunn Nagara, who is Senior Fellow at the Institute of Strategic and International Studies (ISIS) Malaysia.
Source link
Is the future truly Asian?
The Region, while growing fast, faces issues such as youth joblessness, climate change and income gaps
THIS is a question that is at the heart of the tensions across the Pacific.
To Parag Khanna, author of The Future Is Asian (2019), the answer is almost self-evident.
However, if you read his book carefully, you will find that he thinks global power will be shared between Asian and Western civilisations
For the West, the rise of Asia has been frighteningly fast, because as late as 1960, most of Asia was poor, agricultural and rural, with an average income per capita of less than US$1,000 in 2010 prices.
But 50 years on, Asia has become more urban and industrialised, and is becoming a challenge to the West in terms of trade, income and innovation.
Global management consulting firm McKinsey has just published a study on “The Future is Asian” that highlights many aspects why Asia is both attractive to businessmen and yet feared as a competitor.
Conventionally, excluding the Middle East and Iran, Asia is divided into North-East Asia (China, Japan and South Korea), South-East Asia (mostly Asean), South Asia (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh) and Central Asia.
But McKinsey has identified at least four Asias that are quite complementary to each other.
First, there is Advanced Asia, comprising Australia, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea and Singapore, each with per capita incomes exceeding US$30,000 (RM125,600), highly urbanised and rich, with a combined GDP that is 10% of global GDP.
This group provides technology, capital and markets for the rest of Asia, but it is ageing fast.
Second, China is the world’s largest trading economy, second largest in GDP after the United States, and a growing consumer powerhouse. By 2030, the Chinese consumer market will be equal to Western Europe and the United States combined.
China is also an increasing capital provider to the rest of the world.
Third, the 11 countries of Emerging Asia (Asean plus Bhutan and Nepal, excluding Singapore) have young populations, fast growth and cultural diversity.
Fourth, Frontier Asia and India – covering essentially South and Central Asia including Afghanistan – which have 1.8 billion in population, still rural but young.
Taken together, these four Asias today account for one-third of global GDP and 40% of the world’s middle class.
But what is remarkable is that while the region grew from trading with the rest of the world, intra-regional trade has grown faster, to 60% of total trade, with intra-regional foreign direct investment (FDI) at 66% of total inward FDI, and 74% of air traffic.
Much of Asian growth will come from rapid urbanisation, amid growing connectivity with each other. The top 20 cities in Asia will be mega conglomerates that are among the largest cities in the world with the fastest-growing income.
A major finding is that America First-style protectionism is helping to intensify the localisation and regionalisation of intra-regional connectivity in terms of trade, finance, knowledge and cultural networks.
Furthermore, the traditional savings surpluses in Asia basically went to London and New York and were recycled back in terms of foreign direct investment and portfolio flows.
But no longer.
Increasingly, Asian financial centres are emerging to compete to re-pump surplus capital from Advanced Asia and China to fund the growth in Emerging and Frontier Asia.
In short, intra-regional finance is following intra-regional trade.
In a multipolar world, no one wants to be completely dependent on any single player but prefers network connectivity to other cities and centres of activity and creativity.
As Khanna puts it: “The phrase ‘China-led Asia’ is thus no more acceptable to most Asians than the notion of a ‘US-led West’ is to Europeans.”
But are such rosy growth prospects in Asia predestined or ordained?
Based on the trajectory of demographic growth of half the world’s young population moving into middle income, the logical answer appears to be yes.
But there are at least three major bumps in that trajectory.
First, Asia, like the rest of the world, is highly vulnerable to global warming.
Large populations with faster growth mean more energy consumption, carbon emissions and natural resource degradation. Large chunks of Asia will be vulnerable to more water, food and energy stresses, as well as natural disasters (rising seas, forest fires, pandemics, typhoons, etc).
Second, even though more Asians have been lifted out of poverty, domestic inequality of income and wealth has increased in the last 20 years.
Part of this is caused by rural-urban disparities, and widening gaps in high-value knowledge and skills. Without adequate social safety nets, healthcare and social security, dissatisfaction over youth unemployment, access to housing, and deafness to problems by bureaucracies has erupted in protests everywhere.
Third, geopolitical rivalry has meant that there will be tensions between diverse Asia over territorial, cultural and religious differences that can rapidly escalate into conflict. The region is beginning to spend more on armaments and defence instead of focusing on alleviating poverty and addressing the common threat of climate change.
Two generational leaders from the West have approached these threats from very different angles.
Addressing the United Nations, 16-year-old Swedish schoolgirl Greta Thunberg dramatically shamed the older generation for its lack of action on climate change.
“People are suffering. People are dying. Entire ecosystems are collapsing. We are at the beginning of a mass extinction and all you can talk about is money and fairy tales of eternal economic growth. How dare you, ” she said.
The young are idealistically appealing for unity in action against a common fate.
In contrast, addressing the UN Security Council, US President Donald Trump was arguing the case for patriotism as a solution to global issues. Climate change was not mentioned at all.
Since the older generation created most of the carbon emissions in the first place, no wonder the young are asking why they are inheriting all the problems that the old deny.
This then is the difference in passion between generations.
Globalisation occurred because of increasing flows of trade, finance, data and people. That is not stoppable by patriot-protected borders.
A multipolar Asia within a multipolar world means that even America First, however strong, will have to work with everyone, despite differences in worldviews.
All patriots will have to remember that it is the richness of diversity that keeps the world in balance.
The writer ANDREW SHENG is a distinguished fellow with the Asia Global Institute at the University of Hong Kong. This article is part of the Asian Editors Circle series, a weekly commentary by editors from the Asia News Network, an alliance of 24 news media titles across the region.
Source link

Read more:
China in the Asian century - Chinadaily
Hong Kong in decline

 Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Saturday, March 30, 2019
Spotlight on virtual banking licenses
Bank Negara’s plan to issue up to three virtual banking licences has excited the local financial sector which otherwise has begun to look a little lethargic.
The announcement comes at the same time as Hong Kong’s move to issue three licences of this type to a combination of companies partnering finance firms, namely Standard Chartered, BOC Hong Kong Holdings Ltd and online insurance company ZhongAn Online P&C Insurance Co.
Five more of such licences in the city are being processed.
In Malaysia, the announcement by Bank Negara is significant also because the central bank has not issued any new banking licences for many years now.
That said, both Hong Kong and Malaysia’s move to encourage pure online banking ventures is very much in line with the fact that fintech innovations are slowly but surely seeping into the daily lives of people globally, providing cheaper and more easily accessible financial services.
The idea of virtual banks – which theoretically means a bank without any physical branches whatsoever – however, is not entirely new.
In fact, many countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom have attempted it.
Some have failed, others continue to operate, taking deposits and giving out loans much like traditional banking outfits.
Closer to home, India, China, South Korea and Japan have ventured into this model.
Japan, for instance, went for the zero branch strategy as far back as the 1990s with the setting up of Japan Net Bank.
There have been other Internet banks there since then such as Seven Bank which has been providing financial services via ATMs across 7-Eleven convenience shops in Japan since the early 2000s.
In South Korea, the then-chair of the Financial Services Commission, Yim Jong-yong gave initial approval for the setting up of the country’s first two virtual banks back in 2015.
K Bank was its first, starting operations in April 2017 followed a few months later by kakaobank, which started with some W300 billion (about RM1.077bil) in start-up capital.
To be sure, virtual banks, which primarily target the retail segment including the small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), have existed even before the concept of fintech – which is basically using technology to provide improved financial services – gained prominence over the last few years.
The rise of fintech in recent times can be attributed to consumers becoming increasingly tech-savvy and more demanding when it comes to convenience on-the-go.
It also stems from the fact that there are millions of individuals who are unbanked or underbanked but who now have access to the Internet.
In China alone, mobile payments run in trillions of yuan.
It is perhaps this increasing savviness that is contributing to regulators the world over wanting to push for more virtual banks and easing guidelines to fit the concept in.
It is noteworthy that within the Asean region, Malaysia is among the first to attempt this virtual bank model.
Timo, Vietnam’s first bank sans any traditional branch, was officially launched in 2016 while nearest neighbour Singapore currently does not have any banks purely of this nature.Even so, Bank Negara governor Datuk Nor Shamsiah Mohd Yunus has said that the central bank is currently working towards releasing licensing guidelines for such operations only by the end of this year.
She has stressed that discussions with the few parties interested in setting up virtual banks in Malaysia are still at the preliminary stage.
Still, that’s not stopped industry people from raising questions, many of which are valid. For starters, notwithstanding theoretical definitions, what will be the exact definition of a local virtual bank ?
What are the rules?
“Who can apply to operate such banks and will these guys be subject to the same rules that apply to traditional banks such as those involving capital requirements and such?” asks one senior banker attached to a regional bank.
While the jury is still out on rules that will apply in Malaysia should the idea materialise, a broad idea on this can be gleaned from the guidelines that have been set out by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA).
According to the HKMA, firstly, a “virtual bank is defined as a bank which primarily delivers retail banking services through the Internet or other forms of electronic channels instead of physical branches”.
HKMA’s guidelines include rules such as virtual banks having to play an active role in promoting financial inclusion when offering their banking services.
“While virtual banks are not expected to maintain physical branches, they should endeavour to take care of the needs of their target customers, be they individuals or SMEs,” it says, adding that virtual banks should not impose any minimum account balance requirement or low-balance fees on their customers.
In terms of ownership, the HKMA says that because virtual banks will mostly be focused on retail businesses covering a large pool of such clients, “they are expected to operate in the form of a locally-incorporated bank, in line with the established policy of requiring banks that operate significant retail businesses to be locally-incorporated entities”.
It also says that it is generally its policy “that a party which has more than 50% of the share capital of a bank incorporated in Hong Kong should be a bank or a financial institution in good standing and supervised by a recognised authority in Hong Kong or elsewhere”.
While the guidelines cover a lot more, it is worthwhile pointing out that the HKMA is of the view that “virtual banks will be subject to the same set of supervisory requirements applicable to conventional banks”, with some of the rules being changed in line with technological requirements.
It adds that in terms of capital requirement, “virtual banks must maintain adequate capital commensurating with the nature of their operations and the banking risks they are undertaking”.
Noticeable absence of tech players
Interestingly, in the first round of licences given out by the HKMA, there was a noticeable absence of major Chinese tech companies like Tencent Holdings Ltd and Alibaba Group Holding Ltd’s Ant Financial, which many would have thought make obvious choices given their experience in carving out game-changing fintech-centric services especially in their home country of China.
“Mobile payment services offered by the likes of WeChat and Alipay are possible with Internet giants like Alibaba and Tencent behind the entire ecosystem, the fact that they were not included raised some eyebrows,” says one Hong Kong-based banking analyst.
In the same vein, Hong Kong has been criticised for not being proactive enough when it comes to encouraging financial start-ups and being overly protective of conventional banks as evident in its fintech sandbox programme of 2016, which was reportedly introduced to help traditional financial institutions try out new technology instead of supporting fresh start-ups.
“Still, a start is better than no start and we are looking forward to when these virtual banks start operating in nine months’ time,” says the analyst.
He adds that as long as security is not an issue, he hopes that virtual banks will be able to provide what traditional banks are “still not good at”, namely personalised customer service and cheaper services.
While it is early days yet in Malaysia, the general feedback is that virtual banks will be good, specifically for consumers who will have more choices.
But this will come at the expense of increased competition within the banking sector.
Analysts in Hong Kong have predicted that about 10% of revenue belonging to traditional banks there will be “at risk” over the next ten years because of the setting up of virtual banks.
Whether or not it will be the same for Malaysian banks remains to be seen.
A lot of this will depend on the guidelines that the central bank plans to set out in the months to come.
By Yvonne Tan The Star
Breaking ground with new banking concept
 |
| Backed by Ma: MyBank is backed by billionaire Jack Ma’s Alibaba Group Holding Ltd. Alibaba affiliate company Ant Financial owns 30% of the online lender. (Photo: AFP) |
(The Star Online/ANN) - DURING the height of the fintech revolution that’s been taking place over the last few years, one prominent banker in Malaysia made an interesting comment during a private dinner.
The banker said that while he welcomes fintech companies into the market, he wasn’t really afraid of losing any significant business to them. What he really feared, if anything, were the technology giants turning on a banking facility for the millions of users they have on their platforms.
“This Facebook Bank, Google Bank or Whatsapp Financial Group,” he quipped in half jest.
The logic is simple: with those platforms even then having had the myriad users globally, they are able to tap that user group to offer financial services.
But banking remains a highly regulated space. Not every technology company will be able to fulfill those criteria or even have such intentions.
Still, there are a number of virtual banks that have sprung up globally.
Here are some of the more notable ones in this part of the region.
China: WeBank
WeBank is China’s first private digital-only bank, launched in early 2015.
It is backed by tech giant Tencent Holdings – China’s biggest messaging and social networking company, which is also the operator of WeChat
Besides Tencent, its other backers include investment firms Baiyeyuan and Liye Group.
According to its website, WeBank provides consumer banking services through digital channels, as well as microcredits and other loan products.
The Internet-only lender had turned in a profit one year into operation thanks to surging demand for microloans among blue-collar workers and small entrepreneurs.
In 2017, WeBank made a net profit of 1.4 billion yuan or US$209mil, while its return on equity came in at 19.2%.
Its total lending in that year was nearly twice that of closest rival MyBank for the same period.
A recent stake sale of the bank values the company at US$21bil, making it one of the world’s largest “unicorn” companies.
Banking Tech recently reported that the lender is now eyeing an Australian expansion to compete with payments company Alipay, which is its largest rival.
MyBank
MyBank is backed by billionaire Jack Ma’s Alibaba Group Holding Ltd.
Alibaba affiliate company Ant Financial owns 30% of the online lender.
Not unlike WeBank, it has a focus on consumer and small and medium-sized enterprises, a sector underserved by traditional banks in China.
It uses credit data from the e-commerce giant’s AliPay product to conduct analysis for loans.
By circumventing human involvement, the bank said it was able to deliver loans to borrowers faster and up to 1,000 times less than it would cost brick-and-mortar banks to do so.
Like WeBank, it turned profitable one year into operations due to its less capital-intensive model.
Ant Financial is reportedly looking to go public in the near future.
India: Digibank
Singapore’s banking giant DBS Bank launched Digibank in April 2016 – a move that has enabled it to penetrate the Indian retail banking market.
Breaking away from conventional banking norms with their onerous form-filling and cumbersome processes, Digibank incorporates a host of ground-breaking technology, from artificial intelligence to biometrics.
DBS CEO Piyush Gupta expects the mobile-only bank to break even in three to four years, which according to him is not such a bad deal as compared to the traditional branch model, which needs 15 to 20 years to break even.
Digibank has over 1.5 million customers and it is handling them with 60 people rather than the 400-500 staff members it would normally need under the traditional model. Its cost-to-income ratio is in the low 30s.
Following its Indian venture, DBS went on to launch a similar mobile-led bank in Indonesia where the government expects the country’s digital economy to reach US$130bil or about 12% of its gross domestic product in 2020.
Other Singaporean lenders have also jumped on the bandwagon. United Overseas Bank (UOB) said it would launch “digital banks” for its five key markets in Asean, starting in Thailand. It aims to have three to five million customers in the next five years
Elsewhere, OCBC is also reportedly pursuing a similar idea in Indonesia.
Japan
Established in 2008, Jibun Bank reached profitability in less than five years. The outfit is a joint venture between Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ and local mobile network operator, KDDI.
The story goes that instead of competing with each other, the two organisations decided it would make more sense creating a “separate bank” that complement their goals.
The Asian Banker in a case study on Jibun Bank noted that in its first year, the lender had accumulated over 500,000 new customers. By 2015, Jibun Bank’s asset volume surpassed that of Japan’s oldest Internet bank, Japan Net Bank. Asian Banker also noted that the lender’s deposit volume has grown to a size that is comparable to that of a mid-tier regional bank – all of this without the help of a branch footprint.
South Korea: K-bank and Kakao Bank
The two South Korea’s online-only banks have signed up new customers by the millions since beginning operations in 2017.
Kakao Bank is run by mobile messaging Kakao and Korea Investment Holdings, while K-bank is operated by telco KT.
The authorities there are hoping that K-bank and Kakao Bank would spur growth in a banking industry that has stagnated amid rising credit costs, narrowing interest margins and heavy regulation.
The Financial Times in an October 2017 report wrote that about 300,000 new accounts were opened with Kakao Bank in the 24 hours following its launch in late July. This figure was more than what traditional banks in South Korea got in a year through online channels. And as at end-September that year, it had already garnered 3.9 million users.
The news agency said that Kako Bank users can wire money abroad for just a tenth of typical commission fees.
Its peer K-bank, meanwhile, attracted over half a million users in the few months following its April 2017 launch.
In contrast, international banks operating traditional branch networks in the country were looking at downsizing their branches.
Early this year, Shinhan Financial Group inked a deal with mobile app maker Viva Republica to set up an Internet-only bank, making it the third player in the game.
by gurmeet kaur The Star
Related:
 Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM
Rightways - Sowing the seeds of Success:
Think Global, Act Local; Change & Grow Rich; Sow as You Reap & Soar High!
Richard Tan
MBA(UK), BCA(NZ), AMA(USA),MMIM














 llustration: Chen Xia/GT
llustration: Chen Xia/GT